Snell’s Law for Granular Materials
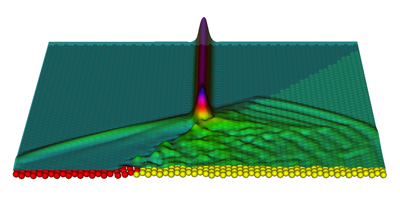
Granular materials like sand and grain sometimes act like solids but also flow like liquids. For example, loosely packed spherical beads resist compression like a solid, but can be stretched effortlessly because the beads just pull away from each other. As a result, such a material acts as a “sonic vacuum” that doesn’t transmit sound. Instead of an oscillating sound wave, a momentary compression generates a “solitary wave” that propagates without spreading. In an experiment reported in Physical Review Letters, Alexander Tichler at the University of Leiden, the Netherlands, and his colleagues simulated what happens when such a pulse crosses between two edge-sharing, two-dimensional materials whose beads have different masses.
When a solitary wave traveling among heavy beads encounters a region of lighter beads, it opens up a fractured region at the interface. The beads from the last row of heavy beads “dance” in this fracture, emitting a series of progressively smaller solitary waves into the lighter beads. The researchers calculated the decreasing amplitude of these pulses by modeling the solitary waves as particles with a particular energy and momentum.
The team also simulated the encounter of a solitary wave with a slanted interface. In general, this collision gives rise to both refracted and reflected waves. The material with heavier beads carries a single wave, while the lighter beads transmit a diminishing series of solitary waves. In spite of this complexity, the researchers matched the results to an equation resembling Snell’s law for light, but with the optical index of refraction replaced by the amplitude-dependent speed of the solitary waves. The results could someday help design structures to shape or deflect medical ultrasound or underwater sonar waves. – Don Monroe