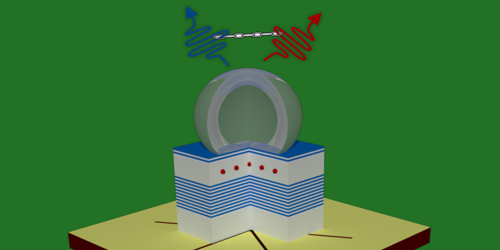
Quantum Dots Serve Entangled Photons on Demand
Quantum communication and computing protocols require sources of photons whose quantum states are highly correlated, or “entangled.” Sources of photon pairs with exceptional degrees of entanglement exist, but they cannot emit such photons on demand. Now, Daniel Huber at Johannes Kepler University, Austria, and colleagues have demonstrated a source of on-demand entangled photon pairs based on nanostructures of semiconducting material known as quantum dots.
State-of-the-art entangled photon sources are based on a process called parametric down-conversion, which converts an input photon into a pair of entangled photons. Such sources, however, emit entangled photons at random times. In contrast, quantum dots can produce entangled photon pairs on demand. But usually the pairs they produce aren’t perfectly entangled because of decoherence of the dot’s quantum states. A particularly detrimental decoherence mechanism is due to an effect known as fine-structure splitting, which spoils the entanglement by scrambling the relative phase of the two emitted photons.
Huber et al. solved this problem with a piezoelectric device that, by applying strain to a GaAs quantum dot, modifies the symmetry of the potential that confines the electrons and holes within the dot, thereby erasing the fine-structure splitting. In experiments, the team found a level of entanglement between emitted photons that was 10% higher than the best quantum-dot sources previously reported and almost on par with that of parametric-conversion sources. These new sources, which are encased in micrometer-thin membranes, could easily be incorporated in integrated photonic circuits.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Mallory Pickett
Mallory Pickett is a freelance writer based in California.