Universe Preceded by an Antiuniverse?
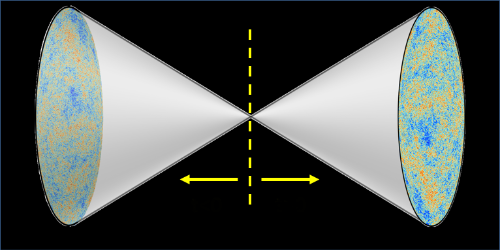
From a certain vantage point, our Universe looks lopsided. Time runs forward as space expands, and there’s more matter than antimatter. This seems to violate a fundamental symmetry, called CPT symmetry, that says physics is unchanged when time, space, and matter-antimatter are all flipped. To balance out the cosmos, Latham Boyle, Kieran Finn, and Neil Turok from the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics in Canada propose that the big bang was also the starting point of an antiuniverse, where time runs in the opposite direction and antimatter dominates. They show that such a CPT-symmetric model is not only consistent with the known cosmic expansion history but also provides a straightforward explanation for dark matter.
The CPT-symmetric model is an alternative to inflation, which assumes that the Universe went through a brief epoch of exponential growth right after the big bang. This rapid expansion can explain certain cosmological observations, but it requires the existence of additional, still hypothetical quantum fields. Boyle and colleagues show that their proposal can explain early cosmic evolution without inventing new physics. In the CPT-symmetric model, time and space flow continuously across the big bang, and the antiuniverse that emerges in the negative time direction behaves like a mirror reflection of our Universe.
The team has yet to show whether this model can reproduce certain observations that the inflation scenario explains—such as the uniformity of the cosmos on large scales. However, the new model gives a natural explanation for dark matter: a CPT-symmetric Universe would produce large numbers of very massive sterile neutrinos. Such superheavy neutrinos might also be the source of recently observed high-energy cosmic-ray showers (see 18 October 2018 Synopsis).
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Michael Schirber
Michael Schirber is a Corresponding Editor for Physics based in Lyon, France.