How to Shape a Single Photon
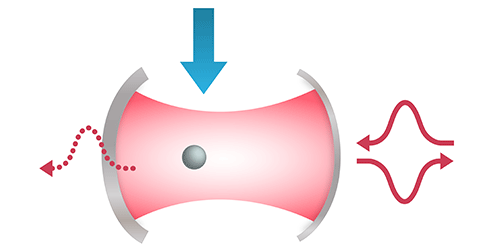
Existing quantum communication devices transmit information using single photons of varying temporal profiles, or “shapes.” But in order for two devices that use differently shaped photons to communicate, the receiving device would have to convert an incoming photon into a compatible shape. To this end, Olivier Morin and colleagues at the Max-Planck-Institute for Quantum Optics, Germany, have demonstrated that they can modify the shape of a single photon via interactions with an atom inside an optical cavity.
First, the researchers trap a single rubidium atom inside the cavity. Then they use a temporally patterned laser beam to tune the interaction between the atom and a single photon entering the cavity. The researchers use a theoretical model to determine the specific laser waveform necessary to make the atom absorb the photon. The same process can make the atom emit a particular photon shape. By combining the operations, the researchers convert a photon from one shape to another.
In a demonstration, Morin and colleagues were able to shrink the temporal width of an incoming photon from 500 s to just 0.5 s and vice versa. They also confirmed the pulse amplitude and phase against the waveform of a common laser reference. The researchers say that their system could help enable a future quantum internet by connecting devices with incompatible photons.
This research was published in Physical Review Letters.
–Sophia Chen
Sophia Chen is a freelance science writer based in Tucson, Arizona.