Topological Defect on the Move
Topological defects are defects that break the order of otherwise ordered systems—think structural defects in crystalline solids or domain walls separating regions of different magnetic orientation in ferromagnets. They affect the properties of the systems in which they arise, but studying how the defects emerge and move is tough to do in a controlled way, especially in the presence of thermal fluctuations. In a new study, Jonathan Brox from the University of Freiburg, Germany, and colleagues report how they have used the exquisite controllability of trapped cold ions to create and direct the motion of a topological defect in a crystalline system.
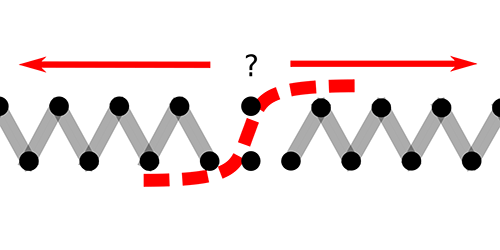
The researchers created a zigzag array of some 30 laser-chilled ions confined in a radio frequency trap. The array has two ground-state configurations, which are mirror images of one another. Realizing both configurations in a single structure requires a domain-wall-like topological defect, or “kink,” between the two. Brox and colleagues generated such a kink and subjected it to thermal noise. They showed that this thermal environment can feed enough energy to the defect to make it vibrate and eventually move down the crystal and exit through one of its ends—which end depends on the kink’s internal structure. They imaged the defect and its motion by scattering laser photons off the ions and collecting them with a CCD camera. The array could be used to study how tiny molecular machines extract energy from a thermal environment in order to move.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Ana Lopes
Ana Lopes is a Senior Editor of Physics.