Particle Acceleration with Multiple Laser Pulses
Accelerating particles to high energies doesn’t necessarily require kilometer-sized accelerators. It can also be done over just a few centimeters using lasers. An emerging technique called laser wakefield acceleration (LWFA) uses a single laser pulse to accelerate an electron bunch to similar energies as those achieved at large facilities. Now, a team led by Simon Hooker at the University of Oxford, UK, has demonstrated a modified LWFA technique that uses trains of laser pulses, rather than a single one. This “multipulse” scheme has the potential to accelerate a thousand times more electron bunches per second than single-pulse methods, which would broaden the range of possible applications.
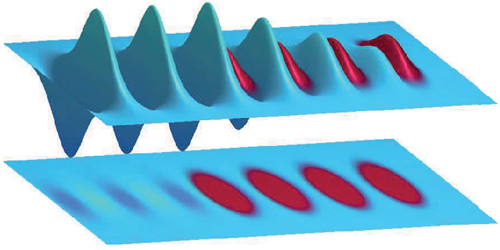
In LWFA, a short, intense laser pulse creates density waves in a plasma. Electrons riding on such waves pick up energy the way a surfer picks up energy from ocean waves. Lasers with sufficient energy to drive this process, however, can only fire a few times per second. Recent theoretical work indicated that trains of lower-energy laser pulses could generate waves that add coherently, providing similar acceleration fields. These pulse trains could be generated at multikilohertz rates. Hooker and his colleagues have now provided the first experimental demonstration of this concept.
By shaping the spectrum of the high-power laser at Rutherford Appleton Laboratory in the UK, the group reconfigured the laser to emit a train of up to seven pulses separated by about 100 femtoseconds. Injecting this into a plasma, they created a plasma wave whose amplitude agreed with predictions from models. In this proof-of-principle demonstration, no electrons were accelerated by the generated plasma waves. However, the group predicts that with optimized lasers the multipulse approach could generate electron beams with repetition rates of several kilohertz and energies comparable to those available at synchrotrons.
This research was published in Physical Review Letters.
–Matteo Rini
Matteo Rini is the Deputy Editor of Physics.