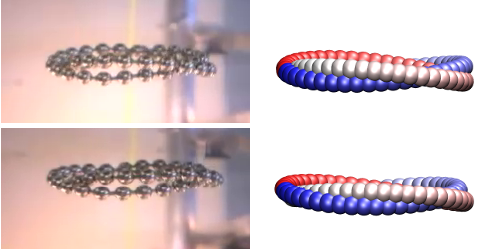
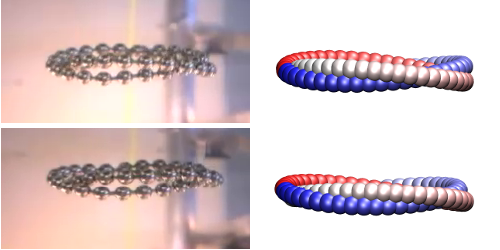
Knotted Loops Fall Flat
Long-chain molecules, like DNA, can develop knots, and these knots in turn affect how the molecules move through a liquid. To understand this behavior, researchers from Poland and Switzerland devised an experiment with loops of small metal beads dropped in a viscous fluid. To mimic the knotted molecular chains, the team arranged each loop to wind around itself in a loose knot. Surprisingly, all the loops settled into horizontally flat configurations as they fell—no matter how they were initially dropped. The results show a connection between topology and hydrodynamics that may help researchers understand the shape evolution of large molecules moving in fluids.
Previous studies of DNA knots have indicated that the speed at which a knotted DNA molecule drifts through a thick gel can be faster or slower depending on the complexity of its knot. Filming this motion directly for nanoscopic DNA would be nearly impossible, so the research team turned to macroscopic loops. The loops, which resemble small beaded bracelets, were formed with multiple loops that intertwined, to create loose, open knots, such as a trefoil knot and a figure-eight knot. The researchers dropped the loops one at a time into a tall cylinder filled with silicone oil. As they fell, the loops evolved from a random jumble of beads into a torus shape consisting of a flattened loop of intertwined strands (see video). These strands swirled around each other in a cyclic pattern. The team also performed numerical simulations and theoretically explained the flattening and swirling of the loops as a consequence of bead interactions mediated by the fluid. The work could provide insight into what happens when large molecules sediment inside a rapidly rotating centrifuge.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Michael Schirber
Michael Schirber is a Corresponding Editor for Physics based in Lyon, France.