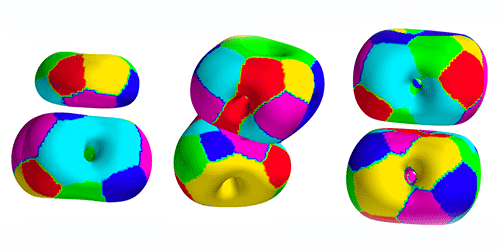Revamping the Skyrmion Model
A famous but flawed model in nuclear physics is getting a reboot. Introduced by Tony Skyrme in 1961, the model describes the nucleus with twists, or “skyrmions,” in a quantum field. This description is attractive because it’s one of few that can be connected directly to quantum chromodynamics, the fundamental theory of quarks and gluons. But while the skyrmion idea correctly predicts some nuclear properties, it is known to miss others. Now, Carlos Naya and Paul Sutcliffe of Durham University in the UK have adapted the skyrmion model and shown that, unlike the traditional version, it correctly predicts the shapes of several light nuclei.
Skyrme’s original concept describes the nucleus in terms of quark-antiquark pairs known as pions. These pions create a quantum field, and the number of twists in this field equates to the number of protons and neutrons (nucleons) in the nucleus. The model correctly predicts some nuclear properties, such as certain allowed quantum states. But it overestimates nuclear binding energies and fails to predict the clustering of nucleons that occurs in some nuclei.
Naya and Sutcliffe’s extension of the model includes rho mesons, which are heavier than pions. With this extension, they compute the nucleon density within nuclei consisting of one to eight nucleons. Their new model not only predicts nucleon clustering effects that the original model misses, but it also predicts binding energies that are 3 times closer to the experimental values. The researchers say their revised model doesn’t provide a “perfect match” with experiments, but it should do progressively better as heavier mesons are incorporated.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Jessica Thomas
Jessica Thomas is the Editor of Physics.