Space-Based Detection of Gravitational Waves Gets Closer
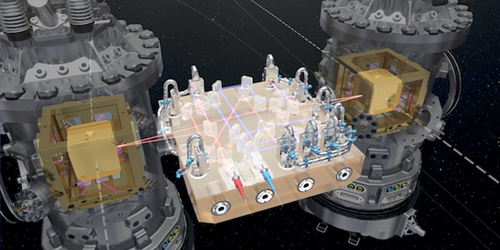
While LIGO and Virgo have grabbed everyone’s attention, researchers are quietly pushing the frontiers of gravitational-wave astronomy into space. In 2015, the European Space Agency launched LISA Pathfinder (LPF)—a spacecraft aimed at demonstrating the technology for a space-based gravitational-wave observatory known as the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA). Following its first tests in 2016 (see 7 June 2016 Viewpoint), LPF has now reported its final results. Experiments onboard the now-deactivated spacecraft have shown that the acceleration of two free-falling masses can be measured with the accuracy needed for LISA.
LISA will observe gravitational waves by measuring how they stretch and compress the distance between two free-falling masses located on different satellites. Such measurements require the test masses to be in almost perfect free fall, isolated from any internal or external forces but gravity. After the 2016 tests, the LPF team implemented a series of improvements in the equipment that protects the masses from spurious forces that might jostle them. For instance, they found ways to reduce the pressure of the gas around the masses, which could create viscous forces, and to suppress the effect of inertial forces deriving from the satellite’s rotation. As a result, compared with the 2016 results, LPF has now improved its acceleration sensitivity by a factor larger than 3 for the frequency range over which LISA is designed to operate. The results bode well for LISA, which will be sensitive to gravitational waves at lower frequencies than those detected so far. Such low-frequency waves could be created by supermassive-black-hole mergers and possibly by the inflationary expansion of the early Universe.
This research was published in Physical Review Letters.
–Matteo Rini
Matteo Rini is the Deputy Editor of Physics.