Galactic Spirals May Form Spontaneously
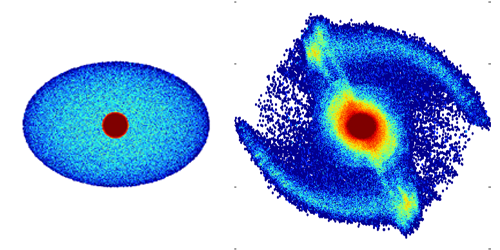
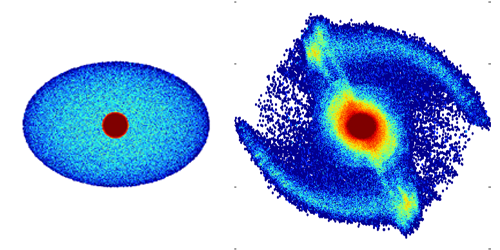
Most large galaxies, including our own Milky Way, have a spiral shape, with a central bulge and an outer disk with several “arms.” No current theory, however, fully explains how these galactic shapes form and evolve. Now, Francesco Sylos Labini of the Enrico Fermi Center for Study and Research, Italy, and colleagues have suggested that spiral galaxies could be transient but relatively long-lived structures formed out of equilibrium from the gravitational collapse of clouds of matter. If confirmed by observations, the result could impact assessments of the dark matter content of galaxies.
In existing models, complex symmetry-breaking effects are invoked to explain spiral shapes, including dissipative nongravitational processes or gravitational perturbations from nearby astrophysical objects. Sylos Labini and his team consider a simpler model in which isolated clouds of particles interact solely through self-gravity, while introducing a small initial rotation and a slight asymmetry of the particle cloud. They find that these conditions can lead to a variety of long-lived but transient structures similar to those found in spiral galaxies.
The fact that galaxies may be out-of-equilibrium systems would have important implications for dark matter studies. A galaxy’s mass—mostly due to dark matter—can be inferred from measurements of galactic rotation using the so-called virial theorem of mechanics, which assumes galactic structure doesn't change in time. If that assumption is invalid, that would affect estimates of the galaxy’s dark matter content. Their model predicts that a spiral galaxy like the Milky Way could expand or contract radially, which the authors say could soon be tested with high-precision measurements of the radial velocities of stars.
This research is published in Physical Review E.
–Matteo Rini
Matteo Rini is the Deputy Editor of Physics.