New Physics Possibilities from Kaon Decay
At the International Conference on Kaon Physics last year, a group of researchers searching for rare forms of kaon decays announced preliminary results that—if confirmed to be signal and not background—defy the standard model. Now, Kohsaku Tobioka of Florida State University, Tallahassee, and colleagues propose three explanations for the unexpected detections that involve new physics beyond the standard model, including the possibility of new particles.
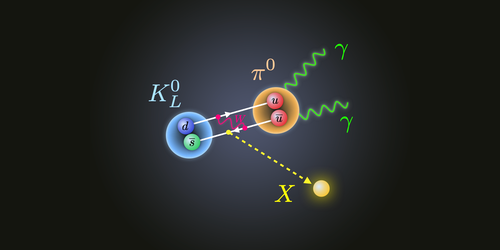
The announcement from the KOTO experiment at J-PARC in Japan related to the detection of four potential instances of a rare decay of the long-lived neutral kaon KL into a pion and two neutrinos—the standard model predicts only 0.1 such events for the experimental run’s sample size. Meanwhile, CERN’s NA62 experiment announced finding no excess events for the equivalent decay of the positively charged kaon K+compared to predictions. Together, these results defy a well-established relationship between the rates of the two decays, which dictates that the KL decay should occur less frequently than its positively charged counterpart.
Tobioka and colleagues came up with three explanations for the results. One proposal includes an additional particle interaction that could make KL decay more often. The other two ideas involve new particles. The researchers suggest that KL might sometimes decay into a pion and an invisible particle X, with that decay masquerading as the one that produces a pion and two neutrinos. Or, they say, KOTO could have witnessed the decay of some unknown particle, and not a kaon.
A special data run at the KOTO experiment this year aims to confirm whether the candidate events were true detections. If they are true, Tobioka says that he and his colleagues will test their proposals to find out which one is correct.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Erika K. Carlson
Erika K. Carlson is a Corresponding Editor for Physics based in Brooklyn, New York.