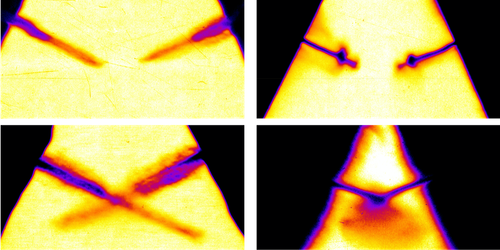
Images Captured of Colliding Microjets
Shine a high-powered laser at one side of a metal foil and a jet of particles will fly out of the other. Researchers have imaged and tracked the particles in these jets to measure, for example, how the type of metal affects the sizes and velocities of the particles. Now, Alison Saunders of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, California, and her colleagues have captured images of two of these jets colliding [1]. Being able to obtain such images opens up many new avenues for experiments, Saunders says, as researchers will be able to study interactions between jets in more detail. Similar interactions occur between particles during planetary formation and other high-energy processes.
To create their jets, the team hit two tin foils with nanosecond laser pulses. The foils were orientated so that, viewed side on, they resembled the pitched roof of a house. Each laser created a shock wave in its respective foil, releasing a 50- -wide, 1-mm-long sheet of tin particles toward the other foil. To image the jets, the team used x rays that they generated by hitting a target with a third laser.
The team collected images of the collisions for jets produced under different experimental conditions. Analyzing these images, they found that for low shock pressures and slow jet velocities (11.7 GPa, 2.2 km/s), the jets passed through one another without attenuation, looking identical before and after the collision point. For higher pressures and velocities (116 GPa, 6.5 km/s), they found that the jets strongly interacted, with the collision producing a cloud of particles. Saunders says that she and her colleagues have yet to understand what causes this change in behavior, but they are excited to find out.
–Katherine Wright
Katherine Wright is the Deputy Editor of Physics Magazine.
References
- A. M. Saunders et al., “Experimental observations of laser-driven tin ejecta microjet interactions,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 155002 (2021).