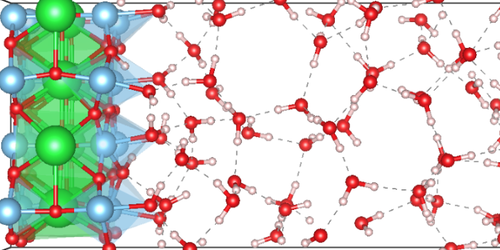
The Brains and Brawn Behind Splitting Water
Hydrogen could be the ideal green fuel. Given its presence in water, it’s an extremely common element on Earth. A single photon of visible light carries sufficient energy to cleave water’s hydrogen molecule ( H2) from its oxygen counterpart. Splitting water this way requires a semiconductor catalyst, within which incident photons excite electrons to higher energy states, providing the electrons and holes necessary for the relevant reactions. But no known material catalyzes those reactions efficiently enough for practical purposes, nor are the reactions’ details well understood. Now a collaboration of experimentalists and theorists has revealed those details for the semiconductor strontium titanate ( SrTiO3), showing that the material has an unexpected cooperation between different facets of its surface nanostructure. The result could aid in creating better catalysts [1].
SrTiO3 can be viewed as a stack of alternating titanium dioxide ( TiO2) and strontium oxide ( SrO) planes. The experimentalists on the team fashioned samples so that the layer that touched the water was either only TiO2, only SrO, or stripes of both, with lines of transition where the two types of surfaces met. Their technique produced silver deposits at water-splitting sites and demonstrated that splitting only happened around those lines.
The theorists then simulated the quantum-mechanical dynamics of the individual molecules. They found that the TiO2 regions were the “brawn” of the operation, contributing electrons and holes with sufficiently high energy. The SrO regions supplied the “brains,” in the form of electron orbitals shaped to shepherd the splitting reaction. Team-member Marivi Fernández-Serra of Stony Brook University, New York, compares the cooperation of the materials to that of a stronger person lifting a more skilled one to swap out a lofty, tricky-to-change light bulb.
–Bob Henderson
Bob Henderson is a freelance journalist based in upstate New York.
References
- V. Sharma et al., “Cooperative interactions between surface terminations explain photocatalytic water splitting activity on SrTiO3,” PRX Energy 1, 023002 (2022).