Improved Readout of Spin Qubits
Quantum computers require a method for determining the states of their computational units, or qubits. Ideally, qubit readout should be fast, accurate, and performed using hardware that facilitates high qubit connectivity. This hardware should also be easy to integrate into the computing architecture. Now two independent teams show how these criteria can be met in the case of a promising type of quantum computer that uses electron spins in silicon as its qubits [1, 2]. The groups’ demonstrations could bring large-scale versions of these machines closer to reality.
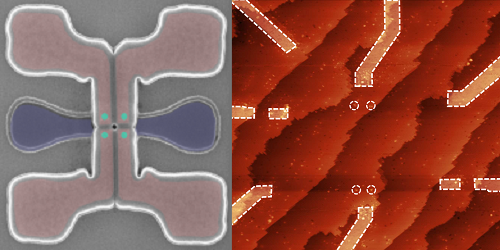
Giovanni Oakes at Quantum Motion Technologies, UK, and his colleagues developed a compact sensor for qubit readout. This detector has a small footprint, needing fewer electrodes than conventional sensors. It also offers high readout fidelity and speed, discerning the correct state of a qubit with 99.2% fidelity in a measurement time of under 6 𝜇s. Crucially, this timescale is much shorter than the typical time it takes for a silicon spin-based qubit to lose its state through decoherence, enabling the implementation of error correction. The researchers produced a detailed model that identifies their sensor’s most important technological parameters for future refinement, and they used this model to show that a fidelity of 99.97% in 1.2 𝜇s should be possible.
Meanwhile, Mark Hogg and his colleagues at the University of New South Wales, Australia, engineered a sensor that is both compact and able to measure the states of multiple qubits. The researchers show that their device can achieve readout of three qubits with a maximum fidelity of 95% and that an optimized version could reach a fidelity above 99%. Moreover, they estimate that the current sensor could be applied to about 15 qubits in a linear array, compared with just 3–4 qubits for current devices. They suggest that this extended range could greatly reduce the number, and therefore the total footprint, of readout sensors in spin-based quantum computers.
Both teams say that their findings will improve the status of silicon spin qubits as candidate building blocks for future quantum technologies.
–Ryan Wilkinson
Ryan Wilkinson is a Corresponding Editor for Physics Magazine based in Durham, UK.
References
- G. A. Oakes et al., “Fast high-fidelity single-shot readout of spins in silicon using a single-electron box,” Phys. Rev. X 13, 011023 (2023).
- M. R. Hogg et al., “Single-shot readout of multiple donor electron spins with a gate-based sensor,” PRX Quantum 4, 010319 (2023).