Pitch-Perfect Corrections for Turbulence
For airliners, encountering turbulence usually results in no more than spilled drinks and startled passengers. But for small aircraft with less inertia—such as drones and future air taxis—sudden air movements can be catastrophic. What’s more, these aircraft are expected to operate in urban environments, where air currents are less predictable. There is therefore a growing need for automatic systems that can quickly and safely steady an aircraft hit by a wind gust. Now Girguis Sedky at the University of Maryland, College Park, and colleagues have demonstrated a system that compensates for sudden air movements by varying the pitch of an aircraft’s wings [1].
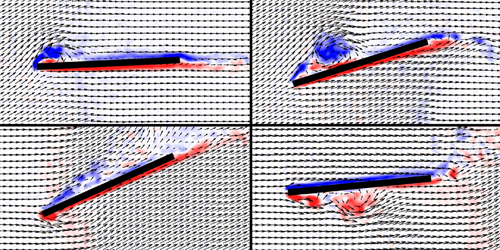
The team focused on correcting for the effects of winds that blow upward across an aircraft’s wings. Such gusts are dangerous because they can cause the airflow to separate from the wings’ upper surfaces—an aerodynamic stall—leading to an abrupt loss of lift. Altering the pitch of the wings can mitigate the effect, but making the right real-time correction is difficult, as pitch changes can induce additional forces that depend on the position of the wings’ axis of rotation.
The team’s automatic feedback system constantly monitors a wing’s lift, comparing the actual value, measured using a force sensor, to the desired one. Any divergence between the two numbers triggers a pitch change. The researchers tested their system by immersing a wing in a water tank and driving it horizontally through an upward-directed current. When the rotation axis was at the wing’s center, the system successfully maintained the wing’s lift in real time. Sedky is now looking at ways to prevent stalling by emulating the wing feathers of birds.
–Marric Stephens
Marric Stephens is a Corresponding Editor for Physics Magazine based in Bristol, UK.
References
- G. Sedky et al., “Experimental mitigation of large-amplitude transverse gusts via closed-loop pitch control,” Phys. Rev. Fluids 8, 064701 (2023).