Tuning conductance
Electron transport through molecules has implications for a range of subjects. In particular, conductance through single-molecule junctions is known to have a complex dependence on atomic structure, orientation, and bonding properties. However, investigations with atomic-scale control of the junction geometry are scarce.
In their paper in Physical Review Letters, Yongfeng Wang and collaborators from Germany, Denmark, and Sweden demonstrate that the conductance in a single-molecule junction varies over orders of magnitude.
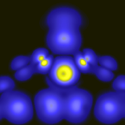
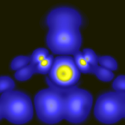
Wang et al. present scanning tunneling microscopy measurements of the conductance of tin-phthalocyanine ( SnPc) adsorbed on a Ag(111) surface in contact with a tungsten tip covered with silver. By manipulating the chemical bonding between SnPc and Ag(111) through selective dehydrogenation of SnPc and an atomic-scale structuring of the electrode, the conductance of single-molecule junctions is varied from 0.013 to 0.32 in units of the quantum of conductance. The authors also perform ab initio calculations combined with a nonequilibrium Green’s function technique for a quantitative analysis of the electron transport through Ag-SnPc-Ag junctions. This opens an avenue to study current flow through single molecules by combining transport measurements with atomic manipulation capabilities of the scanning tunneling microscope. – Sarma Kancharla