Riding Planetary Waves
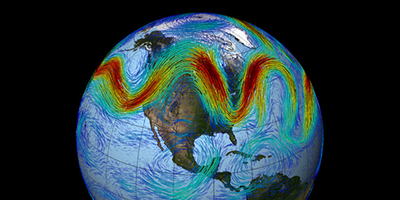
Rossby waves are planetary-scale meanders in the high-altitude winds that flow about above ground (between the troposphere and the stratosphere). They arise because of the temperature difference between polar air and tropical air, together with variation of the Coriolis force with latitude. Meteorologists know them well, as they determine low-pressure systems that have a major influence on the weather. But according to a study published in Physical Review Letters, such waves may determine more than whether it will rain or shine in the short term. By transporting energy around the planet, they may act as important interconnecting links between remote regions, thereby affecting the longer-term dynamics of the climate system.
Yang Wang, at the Bar-Ilan University in Israel, and colleagues describe the climate system using a recently developed approach based on network theory: different regions of the world are considered as nodes of a network, interconnected by links representing the channels through which heat and materials (air and water) are exchanged. The authors apply the method to extract the statistical properties of these links from a database of climate parameters (such as temperature, pressure, and wind velocities) measured during the years 1948–2010. These links exhibit the patterns of an atmospheric Rossby wave: they have undulations that match Rossby wavelengths ( , , and ), are aligned along the same directions, and have the same seasonality.
The finding suggest that Rossby waves might be a dominant channel that connects the climate network—an observation that may make network theory a key component for refining current climate models. – Matteo Rini