Round and Round in Circles
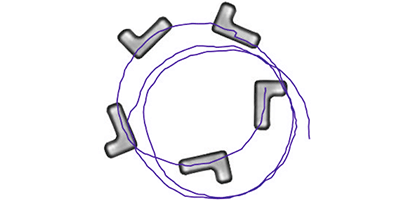
Self-propelling, micron-sized particles can serve as models for real biological swimmers, such as bacteria or spermatozoa. So far, researchers have focused on spherical and rodlike particles, but new experiments with L-shaped particles may give better insight into biological microorgansims that lack symmetry about their propulsion axis. As Felix Kümmel from the University of Stuttgart, Germany, and colleagues report in Physical Review Letters, the experiments show that such particles move in circles in open liquid, but follow a straighter path near surfaces.
Kümmel et al. carved the L-shaped particles from polymer and then selectively deposited gold on the underside of each object’s short arm. When a particle was placed in a solvent mixture and illuminated with light, the gold activated a local demixing of the solvent into its two components (water and lutidine), creating a tiny chemical gradient that propelled the particle in one direction. But unlike symmetric particles, which typically move in a random walk, the L-shaped particles rotated in either a clockwise or counterclockwise circle that depended on the particle’s chirality. Near a wall, however, the particles were seen to either bounce or surf along in one direction, depending on their angle of incidence.
The experimental observations can be understood by considering the viscous forces the fluid exerts on the particles: The particle experiences a velocity-dependent torque that leads to the circular motion, but near a boundary, such as a channel wall, the circular motion is disturbed by the steric particle-wall interaction. This system could provide insight into how odd-shaped microorgansims move through narrow blood vessels or plant veins. – Katherine Thomas