Condensate in a Can
By trapping and cooling clouds of atoms, physicists can control and explore exotic states of matter. The most dramatic example, long predicted but only demonstrated in 1995, is the Bose-Einstein condensate, in which many of the atoms in a cloud share a single quantum-mechanical state. In most experiments to date, however, atoms are attracted by a bowl-shaped potential whose strength varies across the cloud, which makes the condensate more complicated to analyze.
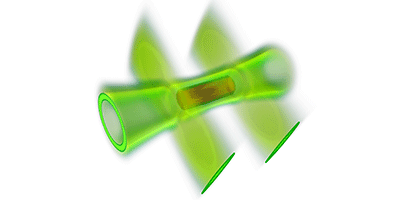
Teams have previously trapped atoms in long, uniform filaments, but in Physical Review Letters, Alexander Gaunt and his collaborators at the University of Cambridge, UK, describe a container that lets the atoms move freely in three dimensions. The researchers first cool a gas of a million or so rubidium atoms in a traditional trap to about a ten-millionth of a degree above absolute zero. They then turn on a green laser to create walls that gently repel the atoms. Part of the repulsive beam is shaped into a cylindrical tube surrounding the atoms, while two other parts form sheets that cap the ends of the tube. The effect of gravity is also canceled, using a small, spatially varying magnetic field.
The researchers confirmed the uniformity of the cloud by measuring the speeds with which atoms fly away when the trap is removed and the temperature at which cooling produces a Bose-Einstein condensate. The uniform trap should make it easier to compare results with theoretical calculations, and also to more accurately mimic other uniform quantum states of matter that are hard to study directly. – Don Monroe