Measuring Nothing
Measuring empty space should be easy—just put a detector out and watch as it doesn’t do anything. In quantum mechanics, things are more subtle because empty space isn’t really empty and, typically, measuring a state destroys it, at least for subsequent measurements. As Daniel Oi at the University of Strathclyde, UK, and colleagues propose in Physical Review Letters, a single atom might be able to signal the presence or absence of the photon field vacuum state without otherwise altering it.
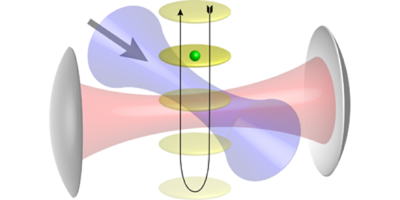
Oi et al. theoretically analyze a single three-level atom coupled to an optical cavity for storing photons. This atom has a special energy-level diagram—one excited state connected to two lower levels by separate transition paths—called a lambda system. One transition (call it A) is excited by a laser while the other (B) is only in contact with the cavity.
With suitable laser pulses, the atom can, in principle, be forced to evolve in a controllable way such that its state depends on the absence of a photon (vacuum) or presence of one or more photons in the cavity. If there is at least one photon in the cavity, and the atom starts in state B, it will end up in state A while pulling out the photon. Conversely, if the cavity is in a vacuum state (empty), the atom will stay in state B, and the cavity stays empty. This setup would allow multiple sequential operations, or could add new photons or extract one photon at a time from an existing cavity field. – David Voss