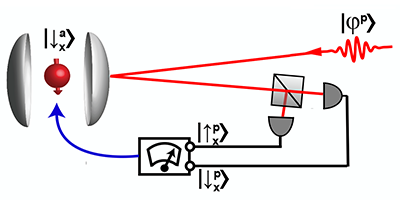
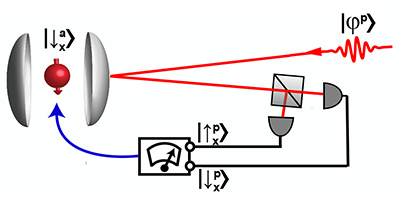
Heralded Qubit Transfer
Optical photons would be ideal carriers to transfer quantum information over large distances. Researchers envisage a network where information is processed in certain nodes and transferred between them via photons. However, inherent losses in long-distance networks mean that the information transfer is subject to probabilistic errors, making it hard to know whether the transfer of a qubit of information has been successful. Now Gerhard Rempe and colleagues from the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics in Germany have developed a new protocol that solves this problem through a strategy that “heralds” the accurate transfer of quantum information at a network node.
The method developed by the researchers involves transferring a photonic qubit to an atomic qubit trapped inside an optical cavity. The photon-atom quantum information transfer is initiated via a quantum “logic-gate” operation, performed by reflecting the photon from the atom-cavity system, which creates an entangled atom-photon state. The detection of the reflected photon then collapses the atom into a definite state. This state can be one of two possibilities, depending on the photonic state detected: Either the atom is in the initial qubit state encoded in the photon and the transfer process is complete, or the atom is in a rotated version of this state. The authors were able to show that the roles of the atom and photon could be reversed. Their method could thus be used as a quantum memory that stores (photon-to-atom state transfer) and recreates (atom-to-photon state transfer) a single-photon polarization qubit.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Katherine Wright