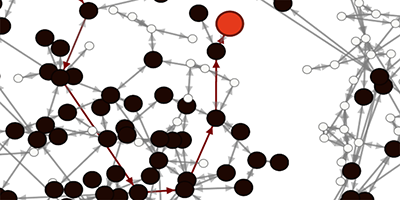
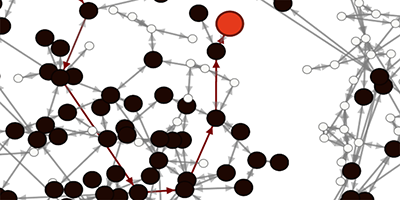
Finding Patient Zero
Identifying the first person to become infected with a disease, “patient zero,” can help determine how, when, and why an outbreak started. A new method developed by Nino Antulov-Fantulin from Ruđer Bošković Institute, Croatia, and colleagues could help pinpoint that person. By comparing a snapshot of the infected population with computations of the spreading dynamics, the model calculates the probability that a given person may be the origin of the disease. While the method cannot unequivocally find patient zero, it could prove useful in narrowing down the origin of an epidemic.
The authors model a population as a network in which each node is connected to its neighbors. An infected node can infect a susceptible neighbor, and once infected, it can recover from the disease. The method works by comparing real-world data on the infected network with simulations of that disease spreading on the same network assuming a given node as patient zero. The model calculates the probability that each node is the infection source and then suggests the most likely patient zero.
Antulov-Fantulin et al. find that their method’s effectiveness depends on how easily the infection spreads, the recovery rate, the size of the network, and the moment at which the snapshot of the epidemic is captured. For rapid disease spreading, patient zero can be located with relative ease with high probability. When the disease spreads more slowly, this probability decreases. Surprisingly, the authors find that patient zero can be difficult to identify in smaller populations where the whole population have been infected. Under these conditions every realization of their simulations is identical, making each node equally likely to be patient zero.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Katherine Wright