Plug-and-Play Photon Source
Many quantum applications that make use of single photons entail transmitting the photons through protective optical fibers. Nicola Montaut and colleagues at Paderborn University, Germany, have designed an application-ready source of pairs of single photons that’s easy to connect to a fiber network. One of the photons in the pair can be used to herald the other’s arrival, a feature needed for quantum cryptography schemes.
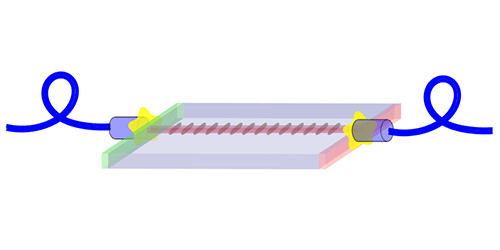
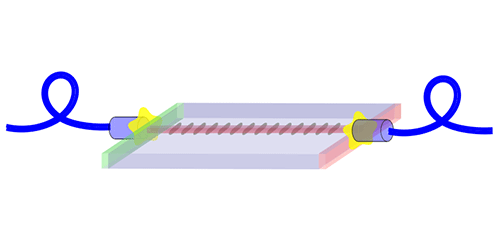
Photon pairs are usually generated through a process known as parametric down-conversion, in which laser light passing through a nonlinear crystal produces two photons with half the laser frequency. If a fiber is to carry away the photons, it must be precisely aligned with the crystal so that the connection doesn’t destroy the photons’ delicate quantum states.
Montaut and colleagues took care of this step. They positioned a fiber with respect to the exit of a high-quality crystal to ensure maximum transmission of light at 1.56 m—the wavelength of the down-converted photons. They followed a similar alignment process for a fiber that carries laser light into the crystal. They also applied a coating to the exit junction to block the laser light, which would otherwise swamp the photon pairs
The team outfitted each end of the crystal with a stretch of fiber, or “pigtail,” so that it can be quickly connected to a laser and a fiber network. As a test of this “plug-and-play” device, they fed it into a splitter that separates the two photons and determined that roughly 50% of the photon pairs were suitable for heralding. This figure is the best of any fiber-coupled source, and it endured after a year of operation.
This research is published in Physical Review Applied.
–Jessica Thomas
Jessica Thomas is the Editor of Physics.