Mirror, Mirror in Free Space
Electromagnetic fields change with boundary conditions around them. For example, a cavity made up of two end mirrors alters the field inside it.
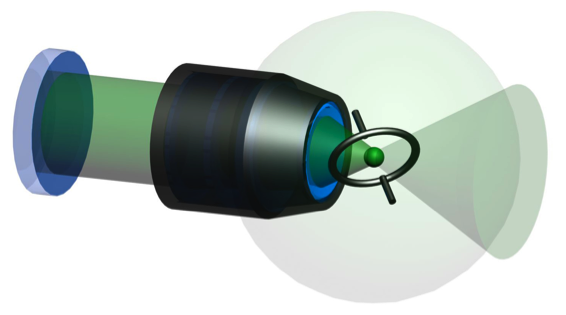
In a paper in Physical Review Letters, Gabriel Hétet and colleagues at the University of Innsbruck in Austria report an experiment in which one mirror of a cavity is replaced by a barium ion cm away, trapped in free space by an applied electric field. The presence of the single mirror alters the field around the atom, which also acts like a mirror and coherently reflects incident light. The experiment demonstrates how the presence of the mirror alters the way the atom couples to the laser light and changes the atomic coupling constant. The group observed that the setup behaves just like a simple cavity with two parallel mirrors, called a Fabry-Pérot cavity.
This part-cavity, part-free-space setup—an advance in the field of cavity quantum electrodynamics—can be used for storage and retrieval of single photons from the atom, necessary for quantum communication protocols. – Sonja Grondalski