Exciting Vibrations
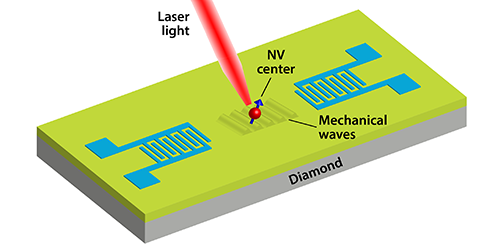
Shine a laser on a nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center—an atomic defect in a piece of diamond consisting of a vacancy (V) next to a nitrogen (N) impurity—and its unpaired electrons jump into an excited state. Andrew Golter and Thein Oo from the University of Oregon, Eugene, and colleagues have shown that these electrons can also be excited using mechanical waves. In this case, the energy of the jump experienced by the electrons can be controlled by tuning the frequency of the mechanical waves as well as that of the incident laser. The authors suggest that mechanical vibrations could be an effective way to control the quantum energy state of electrons in chip-based networks of qubits.
The researchers took a diamond crystal containing a single NV center and built a tiny electrical speaker on the crystal’s surface. By oscillating the speaker, they induced mechanical vibrations in the diamond that traveled along its surface, much like waves on the ocean. As the waves passed over the diamond, they slightly deformed the crystal lattice, changing the spacing and arrangement of atoms around the NV center. When the frequency of the vibrational waves was correctly tuned, the electrons in the NV center absorbed energy from the mechanical waves, as well as from an applied laser, and switched to a different quantum energy state. The authors were able to observe the change in quantum state via photons emitted when the NV center returned to its ground state.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Katherine Wright