Superfluid Storm at a Surface
It turns out superfluids are more like regular fluids than we might have expected. Numerical simulations by George Stagg and colleagues from Newcastle University, UK, reveal that superfluids, which have no viscosity, can form a viscous boundary layer of fluid when they flow past a solid surface, just like conventional fluids do. The result comes on the heels of a recent finding which showed that an everyday flow pattern of vortices dubbed the von Kármán vortex street can also emerge in superfluids (see 7 December 2016 Viewpoint). Taken together, the findings point to stronger ties between the two types of fluid than previously thought.
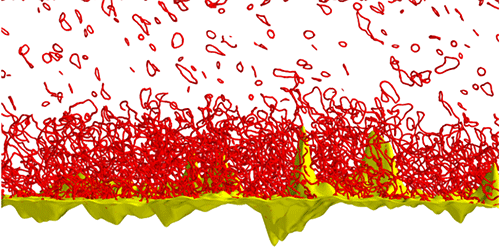
Stagg and his peers modeled the superfluid flow of liquid helium over the surface of a rough wire using the time-dependent Gross-Pitaevskii equation—an equation that’s widely used to describe the dynamics of superflows. The surface of the wire featured a “mountain landscape” of sharp grooves and steep ridges with heights of up to around 10 nm. This profile was that of a real wire used in experiments on superfluid turbulence and was obtained by atomic force microscopy. By running numerical simulations of the model with various flow speeds, the team found that, beyond a critical speed, the superfluid flow did not simply display tiny vortices of fixed size and strength, as is expected for superfluids, but a dense tangle of such vortices. This tangle emerged downstream of the highest mountains on the surface and went on to produce a stormy layer that remained stuck to the surface like a viscous boundary layer in a regular fluid does.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Ana Lopes
Ana Lopes is a Senior Editor of Physics.