Explaining Grid-Cell Firing
The brains of mammals have an internal “GPS” that allows the animals to navigate in the environment. In the hippocampal brain region, neurons called place cells fire electrical pulses when the animal enters specific locations. In the adjacent entorhinal cortex, separate neurons called grid cells fire in regular hexagonal patterns that are thought to form a cognitive map of space. It is unclear, however, how the brain can create these patterns. A new model suggests that they can form through mechanisms similar to those behind many regular patterns seen in nature.
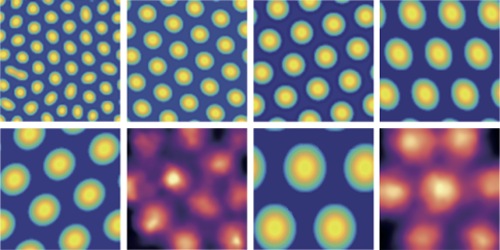
Mauro Monsalve-Mercado and Christian Leibold, both at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, developed their model based on a hypothesis recently proposed by neuroscientists: the firing activity of grid cells may result from that of the place cells. In the model, the movement of an animal in a box generates electrical pulses in place cells, which are fed as inputs to grid cells. The connections between grid cells—and thus their firing patterns—are then altered by neural “plasticity”: each neuron’s connections are weakened or strengthened depending on the timing between the neuron’s input and output.
Running the model’s equations, the authors find that the grid cells’ firing patterns, which are initially random, evolve towards hexagonal configurations as they receive the inputs from the place cells. This process resembles that of pattern-forming phenomena known as Turing instabilities, which are thought to underpin the formation of, for example, zebra stripes and hexagonally shaped bee honeycombs.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Matteo Rini
Matteo Rini is the Deputy Editor of Physics.