Polar Swarms
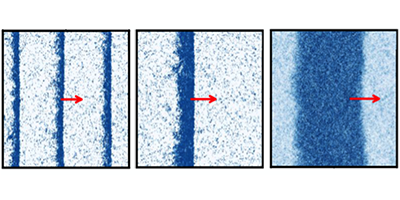
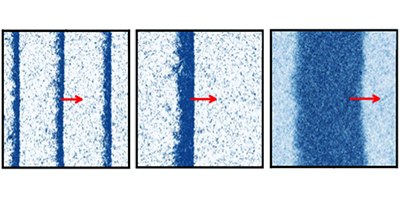
How do individual animals form swarms, schools, and flocks? In the 1990s, physicists modeled collections of self-propelled particles (so-called “active matter”) and could simulate the ordering that occurs in animal flocks. Theoretical models have reproduced many aspects of this collective behavior, but a number of questions have persisted. One concerns the observation that in polar, active matter—think of a collection of small, mutually interacting swimming arrows—the particles organize themselves into three possible pattern classes: density waves, solitary waves (solitons), and traveling “droplets.”
No single theory has been able to explain the formation and diversity of these patterns. However, in a paper in Physical Review Letters, Jean-Baptiste Caussin and collaborators from institutes in France, Germany, and the Netherlands, have solved a hydrodynamic model of polar active particles and have accounted for the origin and variety of these propagating swarm structures.
The authors described a polar fluid’s motion governed by a density field (capturing the distribution of particles) and a polarization field (capturing the polar interactions determined by the direction in which each particle is pointing). By including an effective mean-field potential and frictional forces, the model could reproduce all of the commonly observed patterns. The authors suggest their model provides a “unified theory” of flock patterns—one that allows patterns to emerge as a general feature of the dynamics of polar active fluids, independently of specific model details (e.g., the functional form of the hydrodynamic coefficients). – David Voss