Hydrogen Bonding Comes to the Rescue
When light is absorbed by a biomolecule, it may initiate useful chemical reactions, or cause irreversible damage. Which process dominates depends not only on the molecule, but also on the network of hydrogen bonds that links it to the surrounding solvent or connects different submolecular groups. Russell Minns at the University of Southampton, UK, and coworkers from the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science in Hamburg, Germany, and the Central Laser Facility in Didcot, UK, have now elucidated the role of hydrogen bonding by comparing the effects of light absorption in a hydrogen-bonded molecular complex with those in isolated molecules.
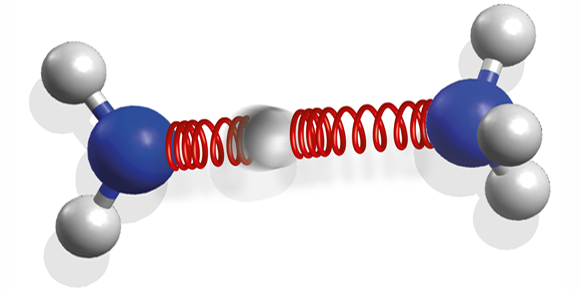
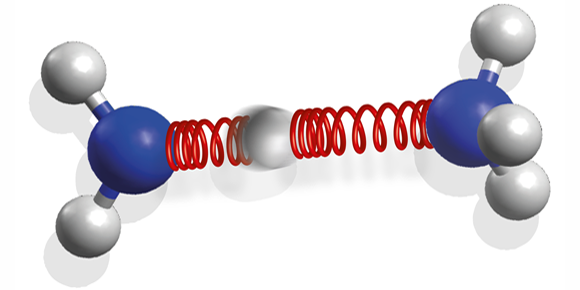
The authors studied the ammonia dimer, two ammonia ( ) molecules held together by a hydrogen bond. The dimer is an important model for larger biological systems because it contains the same hydrogen bond that ties DNA nucleobases together, linking an NH group and a nitrogen atom. The team excited the dimer with UV laser pulses and, using visible-light pulses, measured the dimer’s photoelectron spectrum at different times after absorption. From these, they could infer the molecule's changing structure with femtosecond resolution.
The researchers compared the response of an isolated ammonia molecule with that of the dimer. While the individual molecule breaks apart by losing a hydrogen atom, the dimer remains intact and returns to its original state. This occurs because, instead of dissociating, the molecule undergoes a reversible chemical reaction: it transfers one proton along the hydrogen bond before relaxing to its ground state. A single hydrogen bond can thus stabilize the molecule against photodissociation. The authors suggest that, for biomolecules, this could be a common mechanism for protection against harmful UV light.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Matteo Rini
Matteo Rini is the Deputy Editor of Physics.