Atoms Feel New Force
Atoms can be pushed, pulled, and trapped using laser beams. The light imparts an optical force on the atom that can be utilized to manipulate its position. Now researchers have demonstrated a new kind of atom-acting optical force that squeezes a whole cloud of atoms. Such a collective force could give rise to a cloud that traps itself, or it could allow researchers to modify the density distribution of the cloud in such a way that it focuses other laser beams.
Under the right conditions, a laser photon colliding with an atom transfers its momentum to the atom. Bombard the atom with photons of exactly the right energy, and the atom’s position can be directly controlled. Similarly, lasers can be used to create an electric field that varies in intensity across space. Single atoms that interact with this field feel a force pulling them toward the field’s lowest-energy point. The optical force demonstrated by Noam Matzliah and colleagues from the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel, acts differently.
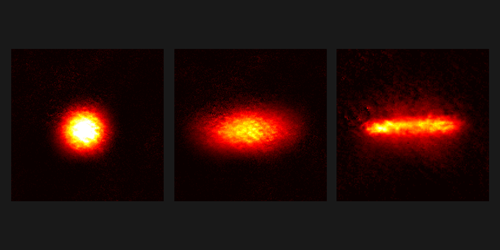
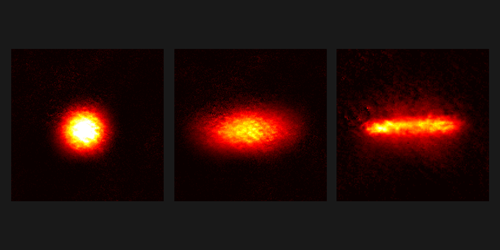
The team illuminated a cloud of one million rubidium atoms with a laser pulse and imaged the atoms’ positions before and after the pulse was applied. They observed the atom cloud elongate in one horizontal direction and condense in the other. The researchers explain this shape change, or optomechanical strain, as a collective effect in which the laser induces forces among all the atoms. This global optical force could allow for the fast, easy tuning of interatomic interactions with lasers, as opposed to the slow, cumbersome tuning possible with current magnetic-field methods.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Katherine Wright
Katherine Wright is a Contributing Editor for Physics.