The Complex Dance of Two-Faced Oscillators
Hang two pendula side-by-side on a wall and their swings slowly shift until they perfectly beat in the opposite direction to one another. Confine a wink of fireflies to the same area and their flashes swiftly fall in step, with thousands of lights blinking in tandem. These so-called synchronization patterns—seen when oscillating objects interact—can take many different forms, but typically each system moves in one particular dance. Now Zachary Nicolaou from Northwestern University in Illinois and colleagues identify a new type of oscillator that can display a variety of synchronization behaviors. The researchers say that this system could be used to model the synchronization dynamics of systems ranging from antiferromagnets to algae.
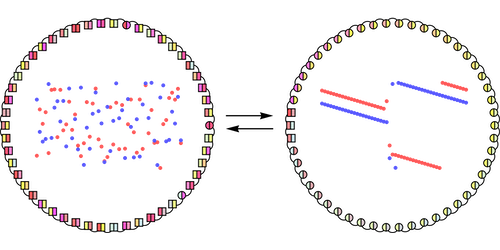
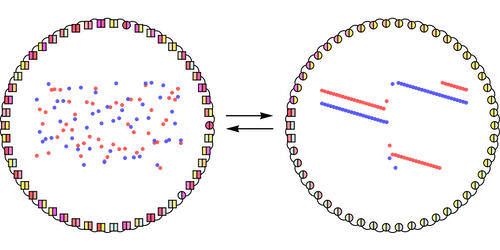
The team considered an oscillator made from two different components. Each component has a distinct natural frequency, meaning that separately they spontaneously oscillate with different periodicities—think of the human body with its beating heart and breathing lungs, which are coupled systems that pulse at different rates. They modeled a ring of 50 of these “Janus” oscillators, named for the two-faced Roman god.
Nicolaou and colleagues predict myriad patterns for Janus oscillators. For example, they find that a ring of identical Janus oscillators, with identical interactions, can suddenly jump from an asynchronous jiggle, where each oscillator moves independently of the others, to one that is synchronized. The likelihood of synchronization increases when the ring consists of unidentical oscillators. Other dances predicted by the team include a variety of “in-between” states, known as chimera states, where one population of oscillators synchronizes while the other remains incoherent. While most of the synchronization behaviors predicted by the team were previously known, they have never before been seen in the same system.
This research is published in Physical Review X.
–Katherine Wright
Katherine Wright is a Senior Editor of Physics.