Mark Buchanan
Matter-Antimatter Molecules
Researchers see hints of the first molecules made from electrons and positrons. Read More »
Fast Bit-Switching in a Thermal Memory
Theorists propose a “thermal” memory—one based on temperature, rather than voltage—that could switch from zero to one faster than other designs. Read More »
Voltage Fluctuations Converted to Electricity
In a step toward the conversion of excess heat into electric current, researchers demonstrate a device that generates current in response to voltage fluctuations that mimic heat. Read More »
Crack Patterns Resemble Fluid Turbulence
A statistical analysis of crack surfaces from three different materials reveals a deep connection with fluid turbulence and a potentially new approach to studying failed machine parts. Read More »
Nanoscale Device Amplifies Fiber-Optic Signals
Researchers have demonstrated an amplifier for near-infrared light that is times more powerful than previous devices and small enough to fit on an integrated circuit. Read More »
Neutrinos Detected from the Earth’s Mantle
About half of the neutrinos detected from natural, underground sources come from the Earth’s mantle, rather than the crust, according to an analysis of new neutrino detection data. Read More »
Shaking Cleans Nanoscale Surface
An oscillatory motion dramatically reduces the number of contaminant molecules at the interface between two surfaces. Read More »
Water Molecules Need Help to Evaporate
Each time a liquid water molecule enters the vapor phase, a coordinated dance of several molecules is involved, according to simulations. Read More »
Burglar Alarm Based on Quantum Mechanics
Researchers demonstrated a scheme that relies on quantum mechanics to prevent unauthorized access to restricted objects, such as nuclear materials. Read More »
Wikipedia Articles Separate into Four Categories
A study of the entire editing history of English Wikipedia shows that the articles cluster into four categories based on how frequently and how aggressively they are edited. Read More »
Background Noise of Gravitational Waves
Assuming LIGO’s recently detected black hole merger is not unusual, researchers revised upward their estimate of the strength of the background noise coming from distant mergers across the Universe. Read More »
Tiny Digital Bits in Ferroelectric Material
Electrons hitting a ferroelectric material can produce a single digital bit 100 times smaller than the bits in today’s commercial memories. Read More »
A Thermostat that Consumes No Energy
Experiments show that a region next to changing hot and cold areas can be maintained at a fixed temperature without consuming energy. Read More »
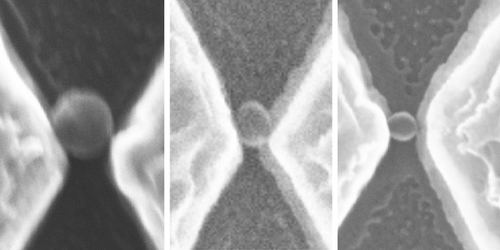
Giant Molecule Made from Two Atoms
Experiments confirm the existence of 1-micrometer-sized molecules made of two cesium atoms by showing that their binding energies agree with predictions. Read More »
Evolution Thins Out Distracting DNA
Proteins sometimes bind to the wrong stretch of DNA, but these "imposter" DNA sequences are statistically rare in many genomes, suggesting that evolution works against them. Read More »
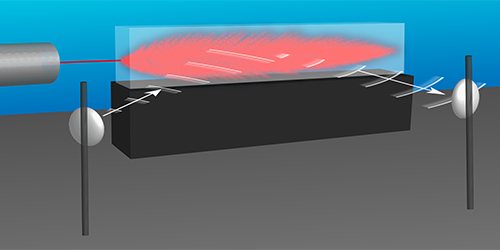
Better Microwaves from a Metamaterial
A system that produces radiation by sending electrons through a metamaterial waveguide could potentially generate high-power microwaves with high efficiency. Read More »
Grid Outages from Failures of Power Line Clusters
Specific clusters within a network tend to fail consistently as part of large-scale network failures, such as those in electrical grids or airline transportation systems. Read More »
Magnetic Fluctuations without a Magnet
Magnetic waves in a permanent magnet can survive even when the material is too hot for large-scale magnetism to exist. Read More »
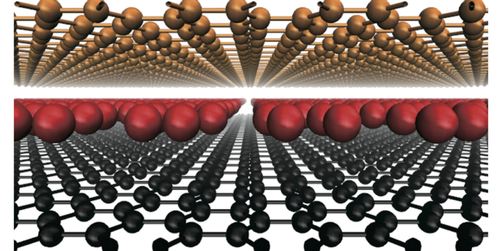
Germanium Revived from the Spintronics Graveyard
Germanium produces a surprisingly large separation of electron spins in response to electric current—good news for spin-based devices, since germanium is highly compatible with silicon. Read More »
Small Space Makes a Strong Electric Field
A carefully shaped air gap in a silicon block would concentrate laser light enough to produce photons that interact with one another, even using a weak laser beam, according to theory. Read More »
New View of Cold Atoms Flowing
A new technique produces an image of the flow of cold atoms through a channel, a potentially important tool for future cold-atom technology. Read More »
Drops Falling in Clouds Make More Drops
Experiments with a simplified version of the atmosphere show that falling drops seed many smaller droplets in their wake. Read More »
Quick Changes in Magnetic Materials
A class of magnetic materials can be reordered at the nanoscale more rapidly than the type usually found in magnetic hard drives, offering a possible route to faster memory devices. Read More »
Dice Become Ordered When Stirred, Not Shaken
A jumble of thousands of cubic dice, agitated by an oscillating rotation, can rapidly become completely ordered, a result that is hard to produce with more conventional shaking. Read More »
Aquatic Eavesdropping
A structured membrane enhances sound transmission across a water-air boundary, allowing underwater sounds to be heard in the air above. Read More »
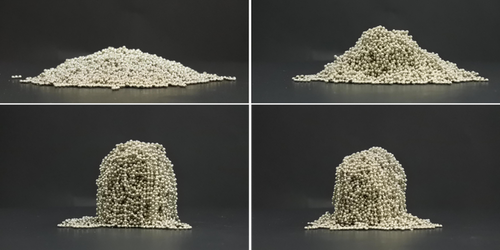
Bead Chains Impersonate Polymer Molecules
Chains of metallic beads act a lot like polymer molecules, even though real polymers are in constant motion. Read More »
How 1000 Bacterial Species Can Coexist
The surprising stability of large and diverse bacterial communities can be explained by a model that emphasizes the microbes’ food requirements. Read More »
Precursor Sounds Warn of Imminent Slip
Distinctive sounds emanate from a material when it is stressed by an outside force and close to slipping—an effect that could lead to warnings of imminent material failure. Read More »
Puzzling Tropical Wind Pattern Generated with Simple Model
2D simulations of the atmosphere, with few assumptions, can generate a slowly oscillating, tropical wind pattern that has puzzled atmospheric scientists. Read More »
The Fastest Spinners
Two teams report spinning nanoscale particles at more than 60 billion rpm, the fastest rotation of any object, with the potential to probe the quantum vacuum. Read More »
More Energy from Ocean Waves
A new structure concentrates water wave motion and could lead to improved techniques for harvesting this renewable energy resource. Read More »
Entangled Photons Sneak through Hole Unscathed
The fragile quantum state of a pair of entangled photons can be protected when the photons pass through a nanoscale hole, which may be useful in future light-based computing. Read More »
How to Study a Speck of Dust
A new technique allows the capture and study of a single dust particle just 34 nanometers wide, nearly 10 times smaller than the previous limit. Read More »
Sound Waves Carry Mass
Even if you ignore general relativity, sound waves transport a small amount of mass, according to theory. Read More »
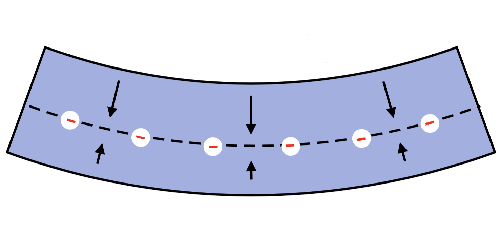
More Voltage from Bending Silicone Rubber
The voltage generated by bending a flexible material is usually small, but a new trick can dramatically increase the effect. Read More »
Longer Movies at Four Trillion Frames per Second
A new technique produces long-lasting movies of nonluminous objects with just a few hundred femtoseconds between frames. Read More »
Thickening Fluid Gets Even Thicker
Adding long polymers to a fluid that becomes more viscous as it’s stirred amplifies the effect, in contrast to results with short polymers. Read More »
Light Seems to Pull Electrons Backward
Light hitting a metal surface at an angle sends the electrons moving in the direction opposite to the light, a result that puzzles theorists. Read More »
Leaf-Like Veins Are Key to Efficient Pump
A network of “veins” improves performance for a leaf-mimicking pump that could be used in microfluidics devices. Read More »
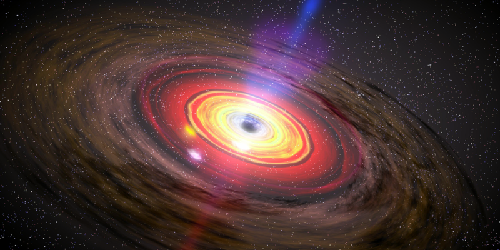
Black Hole Assembly Line
A multiple merger scenario occurring in the centers of galaxies might explain some surprisingly large merger events recorded by gravitational-wave detectors. Read More »
Catching Electrons as They Escape a Liquid
A new technique allows accurate measurements of electrons that escape a liquid surface—information that is essential for understanding chemical reactions in water droplets in the atmosphere. Read More »
Catching Neutrinos on Radar
Radar could detect ultrahigh-energy neutrinos from space, according to experiments using electrons as neutrino stand-ins. Read More »
Wrinkles Turn to Crumples
Thin, flexible sheets in many geometries exhibit the same transition as they are stressed or distorted. Read More »
Space Dust May Not Be So Icy
Dust particles in space may be surprisingly porous, so their surfaces could carry thinner ice coatings and support different chemical reactions than previously supposed. Read More »
Machine Learning Makes High-Resolution Imaging Practical
A new acoustic technique involving machine learning could lead to cheaper and faster high-resolution medical imaging. Read More »
Nanoscale Warming Is Faster Than Cooling
Contrary to conventional wisdom, a sufficiently small, cold object warms to the temperature of its surroundings faster than a warm object cools, according to a new theory. Read More »
Imaging Molecular Structure and Charge Simultaneously
A new technique determines both the charge distribution and the structural distortions that result from the addition of a single charge to a molecule. Read More »
Iceberg Shape Affects Melting
Experiments with large ice cubes show that the melting rate depends on the shape, an effect that climate modelers may need to consider. Read More »
Optics Bench on a Graphene Flake
A nanoscale, graphene-based device takes advantage of the wave nature of electrons and provides a level of control that will be useful for quantum computers. Read More »
Nuclear Spins Detect Subtle Rotations
A small device performs rotational measurements using nuclear spins in a diamond wafer, paving the way for microchip-size gyroscopes. Read More »
Quantum Solution to Classical Drag Puzzle
A quantum-inspired model explains why objects moving in a fluid experience drag even at high speeds where viscosity should be negligible. Read More »
A New Trick to Make Short-Pulse Ion Beams
A new laser technique could lead to ultrashort-pulse, high-energy ion beams for medical use. Read More »
How to Cut into a Material More Smoothly
A theory confirmed by experiments explains what has been an unpredictable cutting process. Read More »
Shape of Melting Ice Depends on Temperature
Experiments reveal that the shape of submerged, melting ice depends on temperature, suggesting that natural ice structures can provide clues about water temperatures. Read More »
The Moon as a Gravitational-Wave Detector
Thanks to a new analysis technique, precision measurements of the Earth-Moon distance should improve estimates of the size of the gravitational-wave background. Read More »
Floating Particle Clump Mimics Asteroids and Nuclei
A disk of plastic particles levitated by sound waves could provide a model for other examples of particle clumps in the physical world. Read More »
Neutrinos from a Black Hole Snack
Researchers have found new evidence that high-energy neutrinos are emitted when a black hole gobbles up a hapless star. Read More »
Quantum-Aided Machine Learning Shows Its Value
A machine-learning algorithm that includes a quantum circuit generates realistic handwritten digits and performs better than its classical counterpart. Read More »
Sound Pulse Drives Single-Electron Current
Like a surfer riding a wave, a single electron is transported by an acoustic pulse traveling along the surface of a microchip. Read More »
Optimizing Flow Speed is Essential for the Gut
Fluid dynamics simulations suggest that the varying flow speed inside the small intestine maximizes nutrient absorption while minimizing excess bacteria. Read More »
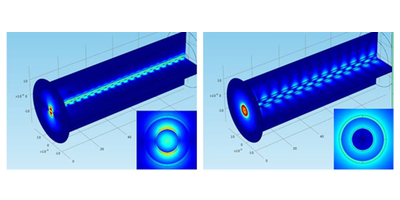
A Möbius Strip for Light
A ring-shaped waveguide with a particular pattern of notches can force a light wave to make two round trips before completing an integer number of wave cycles. Read More »
Meet the Unimon, the New Qubit on the Block
In initial tests, a simplified version of a popular superconducting qubit achieves high computation accuracies, making it attractive for future quantum computers. Read More »
Microsphere Pair Converts Microwaves to Light
A pair of microspheres can convert microwave signals over a wide frequency range into optical signals, which will be essential for future quantum technologies. Read More »
Organelle Building Codes
A new “bursty growth” model for organelles—internal components of biological cells—helps explain observed size fluctuations. Read More »
Why Death Valley Is Full of Polygons
The geometric patterns on dry, salty lake beds are generated by convection of high- and low-salinity water underground, according to simulations and observations. Read More »
“Off Switch” Makes Explosives Safer
An explosive material fabricated with a highly porous structure is inactive but is easily “switched on” when filled with water. Read More »
High-Power, Room-Temperature, Coherent Microwave Source
Magnetic spin excitations can combine with photons to produce exotic particles that emit laser-like microwaves. Read More »
The Optimal Angle for Cleaning with Bubbles
A stream of air bubbles can be most effective at cleaning produce or industrial equipment if it strikes at the correct angle. Read More »
Predicting When a Material Will Crack
A combination of two techniques provides warning signs that the stress on a material will lead to failure. Read More »
Wildfire Predictions from a Water Tank
According to experiments with a fluid model, turbulent air around the treetops could help a wildfire spread. Read More »
Error Rate Reduced for Scalable Quantum Technology
A scalable system for controlling quantum bits demonstrates a very low error rate, which is essential for making practical devices. Read More »
Why Seawater Is Foamy
Observations of air-bubble mergers in water explain why dissolved salt slows this process and leads to foam. Read More »
Nonsteady Illumination Improves Imaging Resolution
Illuminating a high-resolution lens with waves whose intensity diminishes over time can improve the image quality. Read More »
Vanishing Act for Water Waves
Cavities at the sides of a water channel can cause waves to be completely absorbed, suggesting new techniques for protecting coastlines. Read More »
Creating an Audio “Hallucination”
Producing fake sound reflections that simulate the presence or absence of an object could allow the military to hide assets underwater. Read More »
Device Could Lead to New Current-Measurement Standard
High-precision measurements of the oscillations generated by a superconducting device suggest that an improved electric-current-calibration standard should be possible. Read More »
Transition During Winding of a String
As a string winds around a cylinder, a switch occurs from tight winding to looser winding, a behavior that could be relevant for natural phenomena. Read More »
How to Compare Proteins
The motions within the molecule provide a new way to compare the structures and functions of similar proteins. Read More »
Gravity Measurement Based on a Levitating Magnet
A new gravimeter is compact and stable and can detect the daily solar and lunar gravitational oscillations that are responsible for the tides. Read More »
Ocean Measurements Detect Conditions for Giant Waves
Observations of the Southern Ocean show that wind can produce the surface states needed to generate rare “rogue” waves. Read More »
Measuring the First Moments of Crystallization
A new liquid-jet technology enabled researchers to test the theory for liquid freezing more stringently than was possible in previous experiments, but uncertainties remain. Read More »
Theory Predicts Collective States of Mobile Particles
Collections of interacting self-propelled objects held rigidly together show patterns of organized behavior that can be predicted. Read More »
Giant Clams Are Models of Solar-Energy Efficiency
A theoretical model for the illumination of photosynthesizing algae in giant clams suggests principles for high efficiency collection of sunlight. Read More »
Measuring the Rotation of Polluting Plastic Particles
New data on the rotation around both long and short axes of plastic strands may help researchers track and remove microplastics that pollute the ocean. Read More »
How to Detect a Stream of Microwave Photons
A new device converts a stream of microwave photons into an electric current with high efficiency, which will benefit quantum information technologies. Read More »
Ultrafast Lasers Induce Spin Currents Directly
Researchers use ultrashort laser pulses to trigger a spin-aligned electron flow on the few-femtosecond timescale—opening up a possible path toward faster spintronic devices. Read More »