David Lindley
Vibrations and Electrons Team Up in New Quantum Entity
Theorists propose an experiment to observe a “phoniton,” a novel hybrid of an electron and a quantum of vibration in a crystal lattice. Read More »
A New Way to Channel Light
Light passing through a pair of adjacent glass strips generates a slight bending in the material, causing the light to concentrate into narrow tracks. The technique works for all wavelengths of light. Read More »
Landmarks—Lamb Shift Verifies New Quantum Concept
The 1947 discovery of a small discrepancy in hydrogen’s atomic spectrum came at just the right time to push quantum theory forward. Read More »
Landmarks—Atomic Force Microscope Makes Angstrom-Scale Images
The atomic force microscope, introduced in 1986, provided atomic-scale pictures of surfaces, with few limitations on the type of sample. Read More »
Storing an X-ray Photon
A theoretical proposal offers a technique for storing an x-ray photon and releasing it with its quantum properties fully intact. Read More »
Proposed Device Would Shape Magnetic Fields
A proposed design for a cylindrical shell with unusual magnetic properties offers a way to concentrate magnetic field energy. Read More »
Landmarks—Computer Simulations Led to Discovery of Solitons
The 1965 discovery of the isolated waves known as solitons—which appear in many physical systems—was a direct result of the new computer technology available for numerical simulations. Read More »
Pushing a Fullerene through a Nanotube
Placing a water molecule inside a 60-carbon-atom cage creates a structure that can be guided by an electric field. Read More »
Animal Communication Could Support Efficient Foraging
A model mixing Brownian motion with purposeful movement guided by vocal signals suggests that Mongolian gazelle herds may have developed an efficient foraging strategy. Read More »
Gravity Makes the Universe Classical
Weak gravitational waves that fill the Universe are enough to disturb quantum superpositions and ensure that large objects behave according to classical physics. Read More »
Landmarks—The Birth of Photonic Crystals
Periodic structures that control photons, much as semiconductors control electrons, came into being in the late 1980s, through a complex interchange between experiment and theory. Read More »
Superconductor as Nanolattice of Atom Traps
A proposed experiment would trap atoms in a nanoscale magnetic field pattern produced by a superconductor—an arrangement that could perform some kinds of quantum computing. Read More »
Landmarks—Matter and Antimatter are Not So Symmetric
A 1964 experiment on an unusual particle showed a violation of symmetry and led to the conclusion that matter and antimatter are not quite equivalent. Read More »
Landmarks—The Curved Space around a Spinning Black Hole
A novel solution to Einstein’s gravitational equations, discovered in 1963, turned out to describe the curvature of space around every astrophysical black hole. Read More »
Theorists Weigh in on BICEP2
Several theorists discuss the next steps for testing inflation theory following the BICEP2 observations of polarization in the cosmic microwave background. Read More »
Landmarks—Discovery of Particles inside the Proton
High-energy collisions between electrons and protons produced the first indications, published in 1969, that smaller constituent particles lurked inside protons. Read More »
New Type of Turbulence on North Carolina’s Coast
Analysis of sea surface height measurements during a storm in North Carolina’s Outer Banks has led to the first observation of an unusual form of turbulence. Read More »
Saving Space with Quantum Information
A technique that packs the full content of three bits of quantum information into two may be a space saver for quantum computers. Read More »
Landmarks—Ruby Red Laser Light Becomes Ultraviolet
In 1961, researchers showed that laser light could be converted from one color to another, the first nonlinear optical effect, which led to uses ranging from quantum optics to eye surgery. Read More »
Measuring the Spread of Ideas through the Physical Review
An automated analysis of the words in 117 years worth of the Physical Review selects scientific memes—significant ideas that emerge and spread through the literature. Read More »
Nanopyramids’ Color Depends on Viewing Direction
An array of nanometer-sized aluminum pyramids acts as a directional antenna for light, and the direction depends on wavelength. Read More »
Breaking Up Is Hard to Understand
A new experimental technique probes the dissociation of a single molecule in water and reveals more complexities than expected. Read More »
A Detector to Track Antineutrinos
A proposed detector for low-energy antineutrinos would reveal the particles’ trajectories, potentially allowing more detailed studies of Earth’s radioactivity and of nuclear reactors. Read More »
Landmarks—Accidental Discovery Leads to Calibration Standard
The quantum Hall effect, discovered unexpectedly 35 years ago, is now the basis for defining the unit of electrical resistance. Read More »
Metamirror Generates Interference at a Distance
A proposed metasurface made of tiny gold antennas could act as either a flat mirror or a concave, focusing mirror, depending on the radiation pattern of the source, which could lead to new ways to control quantum systems. Read More »
Landmarks—Discovery of a 2nd Kind of Neutrino
A gargantuan experiment in 1962 showed that neutrinos come in two varieties, electron and muon. Read More »
Radio Signals May Reveal Cosmological Structure
Analysis of radio pulses from very distant objects may offer a new way to map the Universe. Read More »
Landmarks—Superconductor Quantizes Magnetic Field
In 1961, confirmation that a magnetic field inside a superconducting ring is limited to discrete values demonstrated that superconducting electrons pair up. Read More »
Landmarks—The Charming Debut of a New Quark
An unexpected particle discovery in 1974 was the first evidence for a fourth type of quark. Read More »
Superfluid Increases Force of Laser Light
Shining a laser onto a microscopic object coated with a superfluid film induces flows that can generate a controlled force. Read More »
Landmarks—Correcting Quantum Computer Errors
In the mid-1990s, researchers proposed methods to preserve the integrity of quantum bits—techniques that may become the key to practical quantum computing on a large scale. Read More »
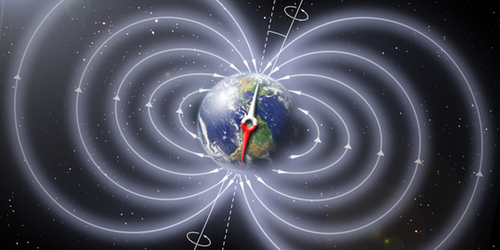
Electric Power from the Earth’s Magnetic Field
A loophole in a result from classical electromagnetism could allow a simple device on the Earth’s surface to generate a tiny electric current from the planet’s magnetic field. Read More »
Keeping a Secret for a Whole Day
Researchers have securely contained a single bit for a record 24 hours, during which it was inaccessible to both sender and recipient, a technology that could be useful for voting or bidding. Read More »
Why Some Gels Shrink under Stress
The gel material that helps blood clot in a wound has anomalous material properties because of the interaction between the gel's fluid and its microscopic fiber network, according to experiments. Read More »
Negative Resistance with a Single Atom
Current flowing through a single silicon atom can be made to decrease with increasing voltage, potentially allowing the integration of a new type of component into microelectronic circuits. Read More »
Celebrated Optical Trick Goes Vibrational
A micromechanical device generates a series of precise, equally spaced vibration frequencies, analogous to the light of the “optical frequency comb,” which has dramatically improved precision measurements. Read More »
Hard and Soft Bounces Explain Asteroid’s Surface Structure
Experiments and computer simulations show that the segregation of small and large rocks on an asteroid’s surface can arise from the way particles hitting the surface collide with the rocks already present. Read More »
Why Sediments Are So Uniform
A new theory suggests that sedimenting particles of irregular shape will drift horizontally as they fall, a result that may resolve a long-standing puzzle. Read More »
Three-Way Detection of Gravitational Waves
The first simultaneous detection of gravitational radiation by the LIGO and Virgo detectors greatly improves localization of the source and permits a novel test of general relativity. Read More »
A Tiny Engine Powered by Light and Liquid Physics
A micrometer-sized sphere trapped by optical tweezers in a liquid, under the right conditions, orbits rapidly around the laser beam—creating a potential micromixing device. Read More »
City Structure Influences Nighttime Temperatures
Mathematical analysis of the two-dimensional layout of a city reveals much about its three-dimensional structure and provides useful measures of the urban heat island effect. Read More »
Barium Ion Detector for Next-Generation Neutrino Studies
A device that can detect individual barium ions could be the heart of an experiment that takes the next step toward probing the nature of the neutrino. Read More »
Friction Remembers Its Origins
Experiments show that the friction between two surfaces depends on their history of contact and that this “memory” is reminiscent of the behavior of glasses. Read More »
Identifying Early Signs of Online Extremist Groups
An analogy between the growth of online networks and the formation of gels suggests ways to detect extremist groups before they become influential. Read More »
A Physical Model for Neurodegenerative Disease
Computer simulations of the diffusion and aggregation of harmful proteins in the brain reproduce the pattern of damage seen in several neurodegenerative diseases. Read More »
Seismic Waves Feel the Moon’s Tug
Seismic measurements reveal the influences of lunar gravitational forces and solar heat on the properties of rocks. Read More »
“Quantum Foam” Scrubs Away Gigantic Cosmic Energy
Theory suggests that empty space is filled with enormous energy, but according to a new proposal, this energy may be hidden because its effects cancel at the tiniest scales. Read More »