Erika K. Carlson
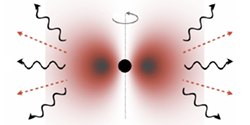
Looking for Dark Matter with Gravitational Waves
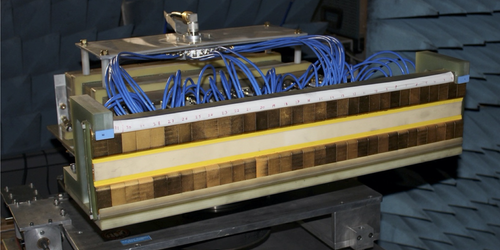
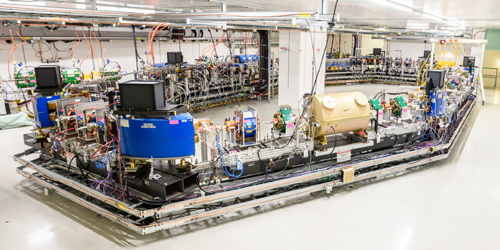
Physicists are building a prototype tabletop detector to capture gravitational waves at higher frequencies than LIGO can and to possibly spot waves from annihilating axions. Read More »
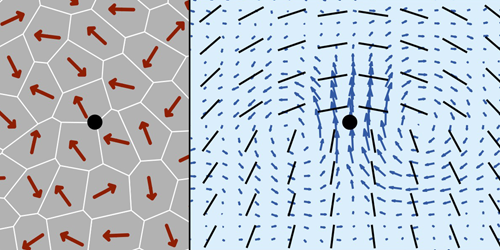
Active Matter that Mimics Turbulence in Space and Time
Despite being driven by a different process, a system of self-propelling particles can evolve over time in a similar way to a turbulent fluid. Read More »
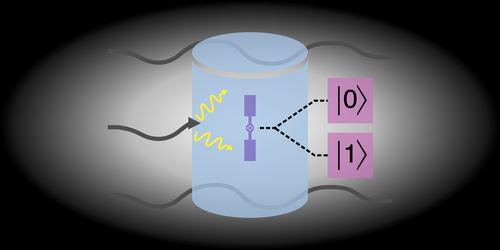
The Key Device Needed for a Quantum Internet
As researchers worldwide work toward a potential quantum internet, a major roadblock remains: How to build a device called a quantum repeater. Read More »
Follow the Crowd to Find a Smell
Simulations show that by trusting their neighbors and following their own “noses,” a swarm of fictitious organisms inspired by moths can quickly find a smell’s source in turbulent air. Read More »
A Statistical Model for Optimizing Output
A new statistical model that optimizes a system’s output could help to maximize the efficiency of mechanical systems. Read More »
The Complex Variability of Climate
Climate scientist Michael Ghil describes gaps in our understanding of climate change. Read More »
Ultrafast, Self-Propelled Particles
New “Marangoni surfers” that whizz along at 10,000 body lengths per second offer new insight into active matter propelled by surface-tension gradients. Read More »
Uncovering How Viruses Evade Cell Defenses
Biophysicist James Hurley studies how viruses, such as the one that causes COVID-19, manipulate cellular membranes to infect cells. Read More »
Protecting Molecular Qubits from Noise
A new proposal for how to encode quantum information in the rotational states of individual molecules could protect these qubits from losing information as a result of noise. Read More »
Sensing Magnons with a Superconducting Qubit
A new method can detect a steady-state population of magnons in a crystal. Read More »
An Intrinsically Magnetic Topological Insulator
Experiments show that the ferromagnetism naturally possessed by the topological insulator manganese bismuth telluride extends right to the material’s surface. Read More »
No Sterile Neutrinos from Eight Years of IceCube
An analysis of more than 300,000 muon neutrino detections provides no evidence of sterile neutrinos—a finding at odds with other experiments. Read More »
A Deeper Understanding of Quantum Thermal Machines
A new theoretical description of how thermal machines work in the quantum regime provides a guide to increasing their efficiency. Read More »
Geometric Inductor Breaks Resistance Quantum “Limit”
A geometric superinductor made of a tightly wound aluminum wire can achieve an impedance about 5 times larger than a hypothesized fundamental limit. Read More »
The First Planetarium Under Kenyan Skies
Susan Murabana brought to life East Africa’s first permanent planetarium using bamboo—a model she hopes will help others build affordable and environmentally friendly planetariums in Africa and beyond. Read More »
Pixels to Stitches: Embroidering Astronomy Images
Astronomers and artists recreate astronomical data with needle and thread. Read More »
The Sounds of Levitating Water Droplets
Leidenfrost drops suspended above a hot surface by a thin layer of vapor emit periodic sounds in a similar way to pipe organs. Read More »
Building Community Among Black Physicists
At the National Society of Black Physicists conference, attendees emphasize the importance of a supportive research community. Read More »
Harnessing Bound Charge in Semiconductors
By controlling the bound charge in a nanowire transistor, researchers hope to improve the performance of these semiconductor devices. Read More »
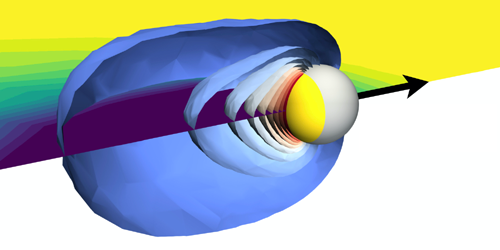
Emitting Radio Waves with Polarization Currents
An unconventional antenna technology can focus the radio waves emitted from the acceleration of polarization currents, aiding use of the waves in communication applications. Read More »
Cooling Hadron Beams with Electron Pulses
Pulsed electron beams can be used to cool beams of ions and protons circulating in a hadron storage ring—a promising development for future high-energy accelerators. Read More »
Capturing the Path of a Light Pulse
Using a megapixel, high-speed camera, researchers reconstructed the complete trajectory of a laser pulse in time and space. Read More »
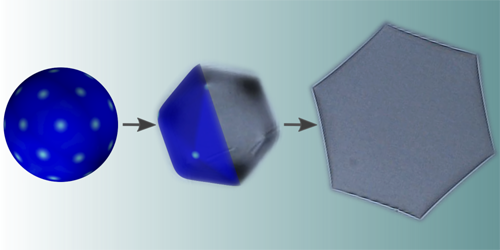
The Strange Shapes of Cooling Droplets
Researchers uncover the mechanism that makes some oil droplets change shape from spheres to icosahedrons to flattened plates. Read More »
Investigating Topological Insulators with High Harmonics
Unlike most conventional materials, topological insulators generate harmonics when driven with circularly polarized lasers, which opens a window on their surface electronic properties. Read More »
Watching an Egg Cook with X Rays
An x-ray scattering technique reveals how egg whites gel on a range of length and timescales. Read More »
Measuring Higher Dimensional “Qudits” for Computation
With a technique called self-guided tomography, researchers accurately measure the states of qudits—quantum systems like qubits but with more than two dimensions. Read More »
A Lower-Pressure Route to Superconductivity
A new synthesis technique pushes high-temperature superconducting materials a step closer to ambient pressure. Read More »
Using Fluctuations to Measure Beam Properties
A new way of measuring a vital property of electron beams helps prepare researchers for next-generation synchrotron light sources. Read More »
Qubits Could Act as Sensitive Dark Matter Detectors
A detector made from superconducting qubits could allow researchers to search for dark matter particles 1000 times faster than other techniques can. Read More »
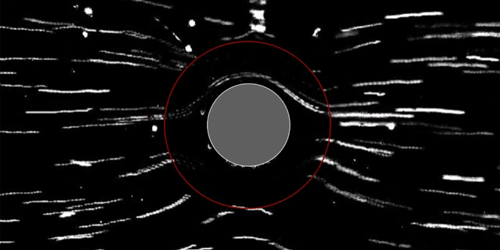
Cloaking and Shielding Objects in a Fluid Flow
By injecting momentum into the fluid around an object, researchers can freely switch between obscuring the object’s presence and canceling hydrodynamic forces on it. Read More »
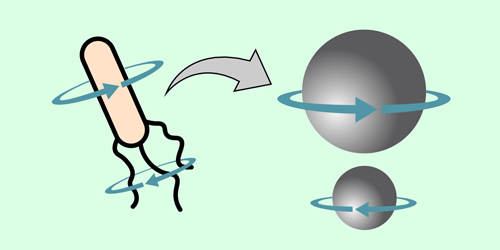
How a Swirling Tail Helps Microbes Swim
A microswimmer that rotates its body and tail in opposite directions can propel itself in elastic, non-Newtonian fluids. Read More »
Experiment Casts Doubt on Potential Dark Matter Find
The DAMA/LIBRA experiment’s potential dark matter detection went unconfirmed for 20 years. Now, a similar experiment offers evidence against the result. Read More »
Cantilever Experiments Update Description of Thermal Noise
Multiple sources of mechanical dissipation seem to explain why a cantilever subject to an extreme temperature gradient has less thermal noise than theory predicts. Read More »
Chromatin May Control How Droplets Form and Grow in Cells
In cell nuclei, molecular structures called chromatin may play a role in the formation of droplets that are crucial for many cellular functions. Read More »
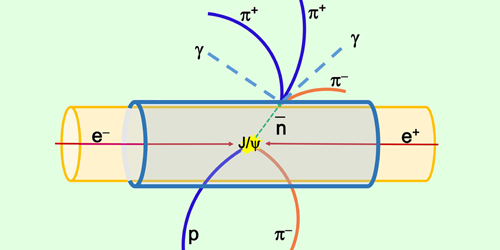
Generating Antineutrons and Hyperons with Existing and Future Facilities
Antineutrons and hyperons are challenging to produce and study, but researchers propose a new approach that would generate these particles using existing and planned accelerators. Read More »
Droplets Propel on Hot Oil
When placed on hot oil films, water droplets self-propel as they boil off, reaching speeds significantly faster than those achieved via most other self-propulsion mechanisms. Read More »
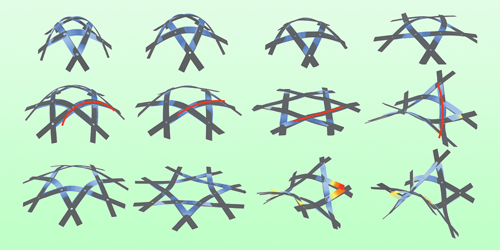
The Geometry of Basket Weaving
Researchers teamed up with an artist to tweak a popular basket-weaving approach, finding a way to weave ribbons to produce any curvature desired. Read More »
Far Fewer Qubits Required for “Quantum Memory” Quantum Computers
Incorporating storage units for quantum information into quantum computers may allow researchers to build such devices with several orders of magnitude fewer qubits in their processors. Read More »
Exponentially Growing Dark Matter
A new model explains the current density of dark matter by proposing that conventional matter converted to dark matter in the early Universe. Read More »
Shock Waves from Ions Damage DNA
Simulations show that the mechanical force of shock waves propagating through cells may be a key component of ion radiation damage to DNA. Read More »
Controlling Phase Transitions in a 2D Model System
Modifying surface and boundary features lets researchers control how a 2D model system transitions from a fluid to a crystalline phase. Read More »
New Unstable Nucleus Detected
Experimental detection of the unstable nucleus magnesium-18 hints at a weakening of the so-called magic number for the closed shell of eight neutrons. Read More »
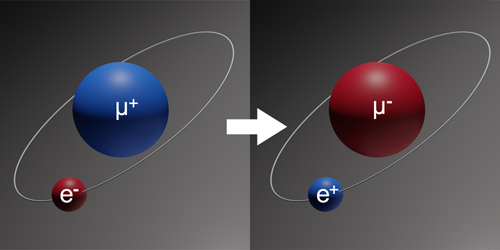
Evaluating Models of the Muonium-to-Antimuonium Transition
By investigating models of physics beyond the standard model, researchers determine the parameter spaces where future experiments might detect—or rule out—a new interaction. Read More »
Lizard Scale Patterns Described with Antiferromagnetic Model
The pattern of green and black scales on an ocellated lizard can be described with the two-parameter Ising model for antiferromagnetic systems. Read More »
Extending and Contracting Cells
Cell-substrate interactions explain a difference in behavior between individual cells and tissues on a surface. Read More »
Sneak Preview of Early Quasar Observations
The newly launched James Webb Space Telescope should be able to see the galaxies that house some of the Universe’s earliest supermassive black holes—according to a new analysis. Read More »
Boosting the Performance of Quantum Repeaters
Multiplexing techniques could boost the chances of achieving end-to-end entanglement of a signal in a trapped-ion-based quantum-computer network. Read More »