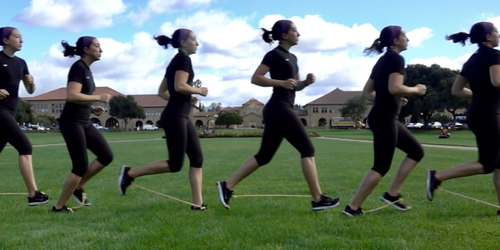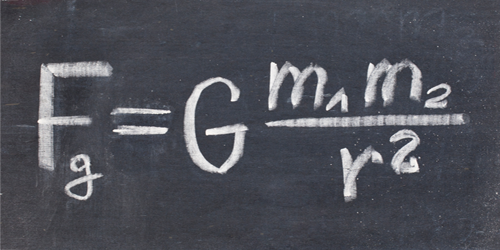Michael Schirber
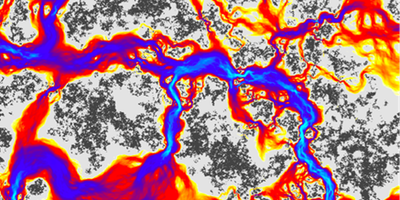
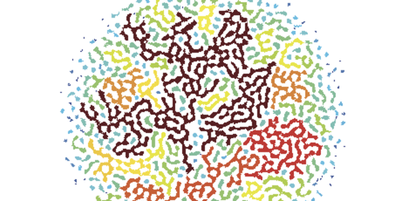
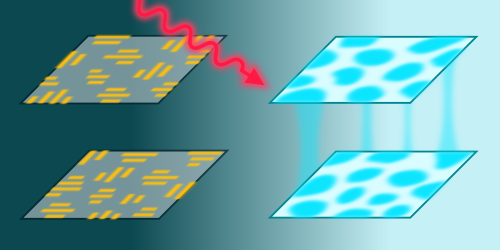
Hiding Secrets in Spontaneous Patterns
A new, secure way to send messages camouflages them inside the same kind of self-organizing patterns that appear in vegetation patterns and the stripes on animal coats. Read More »
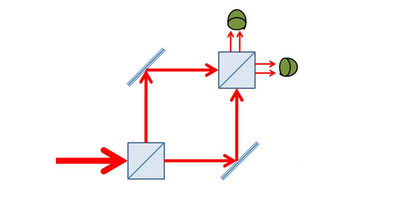
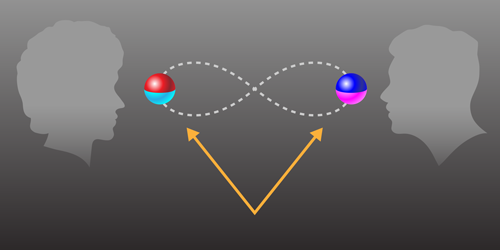
Another Step Back for Wave-Particle Duality
A new thought experiment makes it clearer than ever that photons aren’t simply particles or waves. Read More »
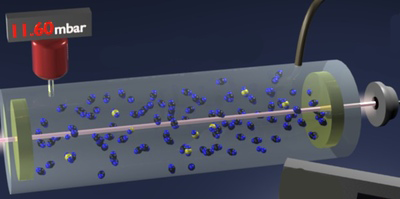
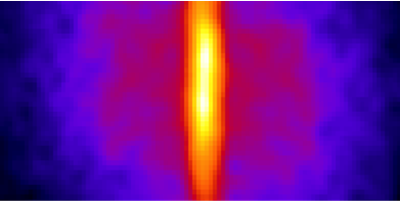
Carbon Dating with Lasers
Infrared spectroscopy can detect trace gases and potentially provide an alternative carbon dating technique. Read More »
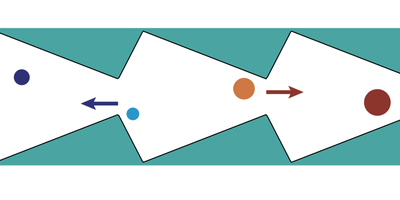
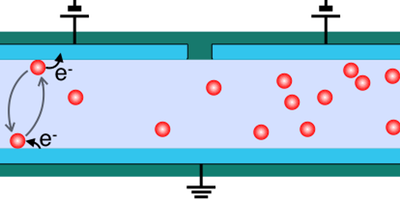
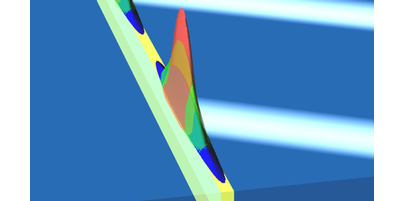
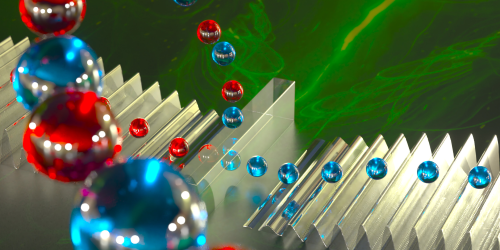
Particles Sorted by Entropy
A proposed device improves on past designs and would sort small particles from large ones to a purity of over 99 percent, without any moving parts. Read More »
Landmarks—Millikan Measures the Electron’s Charge
The Millikan oil drop experiment, published in final form in 1913, demonstrated that charge comes in discrete chunks and was a bridge between classical electromagnetism and modern quantum physics. Read More »
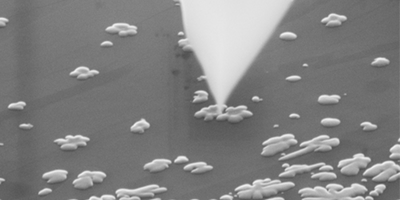
Why Salt Clusters Form on Basement Walls
Salt crystallizing on walls or old artifacts forms in discrete bunches, rather than coating the surface, because of an unexpected feedback effect, according to experiments and simulations. Read More »
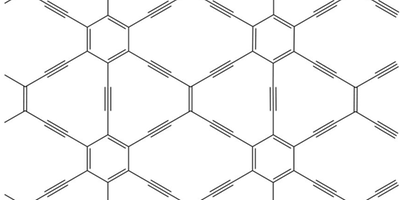
Graphyne May Be Better than Graphene
Sheets of single-layer carbon with a variety of bonding patterns may have properties similar to the wonder material graphene, according to new computer simulations. Read More »
Nuclei Emit Paired-up Neutrons
A neutron-rich nucleus can emit a neutron pair as a single unit as a product of nuclear decay. Read More »
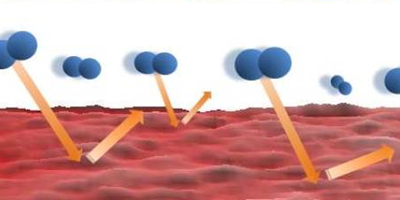
Cooling with a Warm Glow
Incoherent light from the sun or from an LED could cool a small object, according to two theory papers. Read More »
Curling Physics Unraveled
Experiments and simulations lead to a new model for the curling of a thin strip, which could be useful for plant growth and micromechanics. Read More »
Electron Spin Influences Nanotube Motion
The oscillations of a carbon nanotube can strongly affect the spin of an electron trapped on the tube, and the tube can also be affected by the spin, according to theory. Read More »
Plugging Leaks in Seal Models
Gaskets and other seals can stop leaks even if the leak-preventing surfaces have just 42 percent of their area in contact at the microscopic scale, according to computer simulations. Read More »
Measuring the Smallest Trickle
Researchers used a nanoscale tunnel in a silicon chip to measure a flow rate of a few picoliters per minute, which is smaller than any previous observation. Read More »
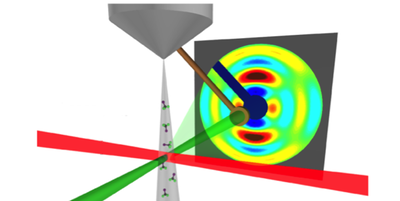
First Frame from 3D Molecular Movie
In a step toward 3D movies, researchers have combined short laser pulses with electron diffraction methods to rapidly map the structure of a simple molecule in three dimensions. Read More »
Nobel Prize—Tools for Quantum Tinkering
David Wineland and Serge Haroche, who studied photons and atoms in new ways, have won the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physics. Read More »
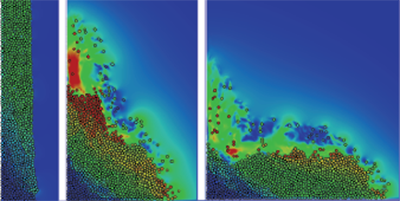
Model of Tumbling Sand Castles
Two-dimensional simulations provide the first element-by-element accounting of the fluid and grain flow in an underwater avalanche. Read More »
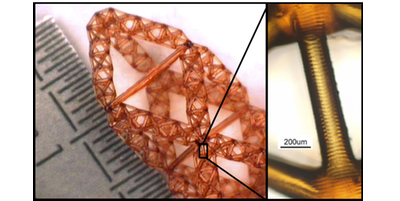
Fractal Structures Do More with Less
Calculations show that the weight of large support structures can be dramatically reduced if their design consists of patterns that are the same at large scales as at the tiniest scales. Read More »
Subterranean Sound Waves from Projectile Impact
A projectile striking granular material generates a series of acoustic pulses that propagate down from the impact site. Read More »
Tuning the Flow through a Soap Film
An electric field applied to a soap film induces fluid flow through the film and causes its thickness to increase—a phenomenon that could be useful in microfluidic systems. Read More »
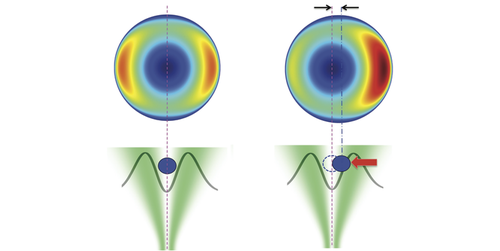
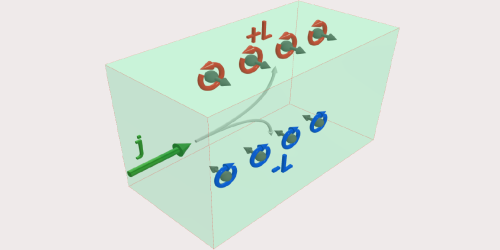
Atoms Organize Themselves
A theoretical model finds that atoms can organize themselves into a regularly spaced row when trapped between a pair of nanosized optical fibers. Read More »
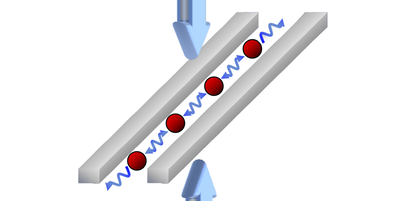
Ultrasound Signal Reveals Microstructure
A model for analyzing materials using ultrasound shows that the seemingly random fluctuations in the data may contain information about the microscopic structure. Read More »
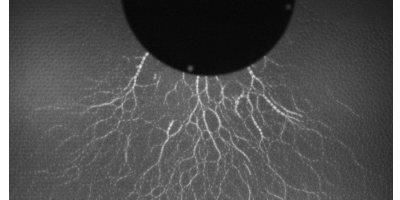
Windshield Cracks Hold Secrets of Impact
Firing projectiles at plates of glass or plastic shows that the number of resulting cracks is an indicator of the impact velocity and of material properties. Read More »
Controlling Persistent Stress in Glass
Internal stress in a glass material is an important source of strength. Theory and experiments provide a new molecular-scale understanding of the process by which such stress develops. Read More »
Designing Better Materials for LEDs
Researchers designed and synthesized an organic molecule whose electronic structure helps funnel energy into fluorescent emission. Read More »
How to Learn a Language Quickly
Simulations show that you can learn the meaning of words rapidly if you assume that every object has only one word associated with it. Read More »
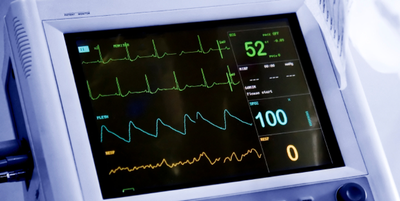
Modeling the Not-So-Steady Heart
Mimicking the stable but not perfectly periodic beating of the heart and similar biological systems requires a new kind of mathematical model. Read More »
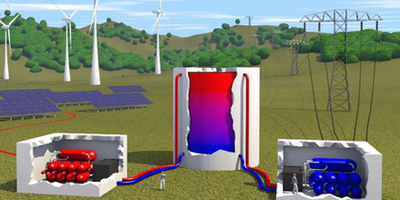
Packing Heat to Store Energy
A theoretical analysis explores the efficiency limits of a method for storing electrical energy from a power plant by heating up a tank of fluid. Read More »
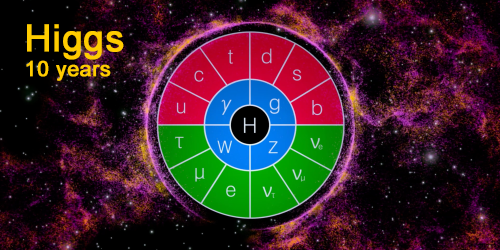
Nobel Prize—Why Particles Have Mass
The 2013 Nobel Prize in Physics has been awarded to two of the theorists who formulated the Higgs mechanism, which gives mass to fundamental particles. Read More »
Controlling Flow with a Roughness Knob
A new technique for controlling gas flow through microchannels involves adjusting the surface roughness of a thin film coating the walls. Read More »
Dragging Nanoparticles Reveals Extra-Low Friction
Experiments demonstrate the breakdown of one of the basic laws of friction at the atomic scale, where more slippery conditions prevail. Read More »
Bleaching Cleans Up Cell Images
The resolution in a biomedical imaging method can be improved by over-exposing, or “photobleaching,” some of the signal-producing molecules. Read More »
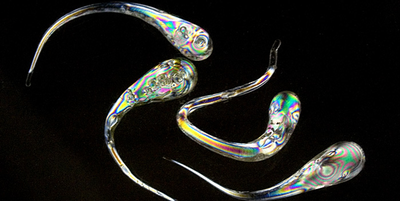
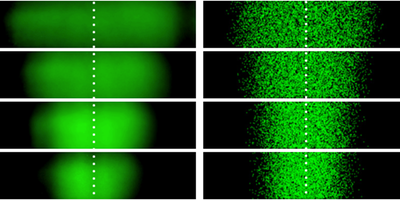
Turbulence Can’t Stir Plankton
Turbulence causes certain swimming microorganisms to segregate into clusters, rather than spreading out evenly, according to experiments and simulations. Read More »
Neutrinos Are Brighter at Night
The solar neutrino signal from a Japanese detector is slightly stronger at night because neutrinos traveling through the Earth behave differently than those that reach us directly from the Sun. Read More »
Plant Gas Valve under the Microscope
Precision measurements of plant microstructures provide new insights into how they prevent gas bubbles from disrupting water flow. Read More »
Light Nearly Stopped in a Waveguide
Calculations show how to excite extremely slow-moving light pulses in a nanosized waveguide. Read More »
Cutting Losses for Surface Light
Light sent along metal surfaces—inside a future optical computer, for instance—may undergo reduced losses if the emitter is a thin slit or hole, experiments show. Read More »
Electrons Not the Cause of Charged Grains
Experiments show that the buildup of charge in a collection of grains is not due to the transfer of electrons. Read More »
Plasma Extremes Seen through Gas Bubble
Sound-stimulated gas bubbles in liquid become tiny plasmas and may provide a test bed for plasma physics theories. Read More »
Nuclear Monitoring with Antineutrinos
A system to monitor a nuclear reactor for possible diversion of weapons material would use an antineutrino detector parked close to the facility. Read More »
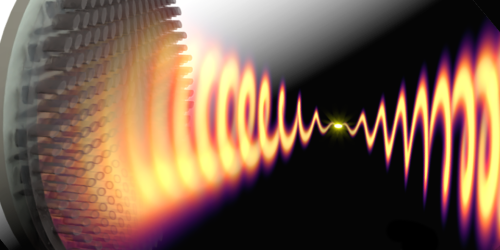
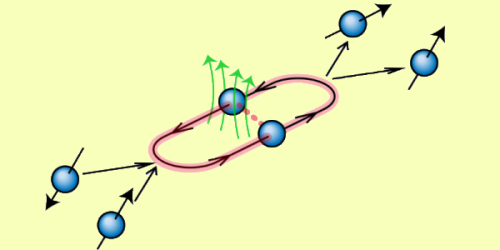
Curvy Photon Trajectories Could Be Detectable
Quantum mechanics permits particles to follow bizarre, looping and curving trajectories, usually with very low probability. But a calculation shows that in some cases, these paths can have significant and possibly measurable effects. Read More »
Nobel Prize—Seeing Single Molecules
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry recognizes the development of super-resolved fluorescence microscopy. Much of this field can be traced back to the first detection of single molecules in solids. Read More »
Fluid Jet Acquires Wings
A high-speed jet of certain fluids will form multiple wings, or archlike structures, when hitting a solid surface. Read More »
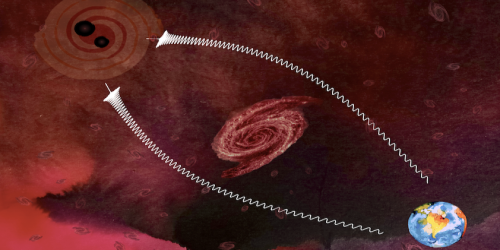
Gamma-Ray Bursts Determine Potential Locations for Life
Powerful stellar explosions may have caused mass extinctions on Earth and could also have prevented life from appearing on other planets until 5 billion years ago—and then only in the outskirts of galaxies. Read More »
Why Language Exceptions Remain the Rule
Interaction among speakers of a language may explain why frequently used verbs tend to remain irregular even as language evolves over generations. Read More »
Laser Filaments Go through Phase Transition
A powerful laser beam separates into many smaller filaments that undergo a phase transition similar to fluid percolating through a porous material. Read More »
Single-Frequency Mirror
A mirror made with metamaterials reflects at a selected angle and only responds to radiation of a specific frequency, while being transparent to other radiation. Read More »
How to Stop a Nanosphere
Combining two trapping techniques reduces the motion of a levitated bead close to the point where quantum effects should become observable. Read More »
Liquid Helium Brewed Locally
A new device for recycling the helium coolant in an MRI scanner or similar machine uses elevated pressure to dramatically increase the rate at which helium is liquefied. Read More »
Pulses Give New Force to Probe Microscopy
A new technique in atomic force microscopy more accurately measures the electrostatic force between the probe and the surface. Read More »
Energy Boost from Black Holes
Particles orbiting near a spinning black hole might collide and get ejected with much more energy than previous calculations showed. Read More »
Understanding a Spreading Puddle
Classical fluid theory can't explain a puddle that spreads and then stops. A new theory solves the problem by incorporating intermolecular forces between the liquid and the solid underneath. Read More »
Measuring the Forces in a Knot
Knots tied with stiff wire have a simplified geometry that reveals the relationship between the configuration of a knot and the forces within it. Read More »
The Difference Between Round and Square Pipes
Calculations of the motion of particles carried by a fluid flowing through a pipe find a surprising effect of the pipe's shape. Read More »
Stalling a Molecular Motor
Researchers used a viscous fluid to disrupt the operation of a molecular motor that transports material inside biological cells, giving insights into how it works. Read More »
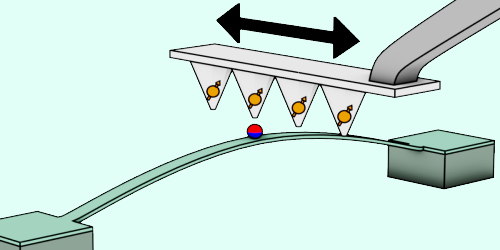
Optical Funnel Traps Particles
Light-induced thermal forces could funnel a stream of proteins or viruses into the small target space of an x-ray laser for single-particle imaging. Read More »
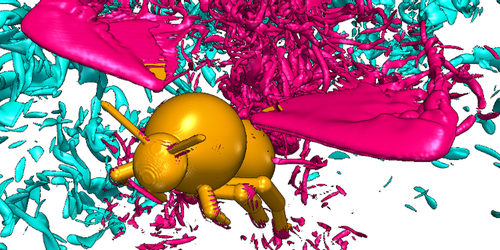
Bumblebees In Turbulence
A simulation of a flying bee shows that insects don’t expend extra energy to maintain lift in turbulent air flow. Read More »
Eroding Grains Step by Step
Experiments with an eroding stream of grains reveals a step pattern that implies the erosion is governed by collisions rather than friction. Read More »
Polariton Laser Upgrade
The emission from a polariton laser shows the coherence that is common to conventional lasers, a step toward using them as high-efficiency alternative light sources. Read More »
Space Wave Gives Electrons a Shove
A new satellite mission has observed electron acceleration by electric field waves moving along the magnetic boundary between the Earth and the solar wind. Read More »
Water Molecule Spreads Out When Caged
Water molecules confined in nanochannels exhibit tunneling behavior that smears out the positions of the hydrogen atoms into a pair of corrugated rings. Read More »
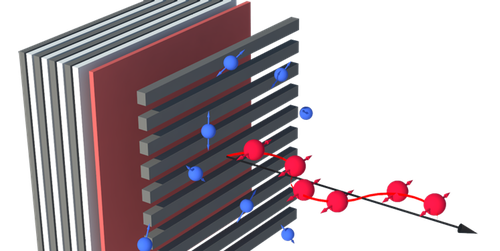
Low Cost Polarized Positrons
A new technique requires much less energy to produce a beam of polarized positrons than previous techniques, making such beams potentially more widely available. Read More »
Balls as 3D Gears
Spinning a few spheres among a large collection of them can lead to a predictable state where each sphere rotates in synch with the others. Read More »
Detecting Photons With a Thermometer
A new technique detects as few as 200 microwave photons at a time by the heat they supply to an electrical circuit. Read More »
Smoke Rings in Light
A newly discovered optical vortex forms a ring around many intense laser pulses but was never noticed before. Read More »
Nobel Prize—Topological Phases of Matter
The 2016 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to theoretical physicists whose work established the role of topology in understanding exotic forms of matter. Read More »
Light Switched Off by Weaker Beam
An all-optical switch design uses an asymmetric waveguide that reduces the beam power requirements, which is essential for making such devices practical. Read More »
Measuring Gravity with an Atom Chip
A new gravity-measuring device uses ultracold atoms generated by a centimeter-wide atom chip, which might lead to a shoebox-sized gadget. Read More »
More Hints of Exotic Cosmic-Ray Origin
New Space Station data support a straightforward model of cosmic-ray propagation through the Galaxy but also add to previous signs of undiscovered cosmic-ray sources such as dark matter. Read More »
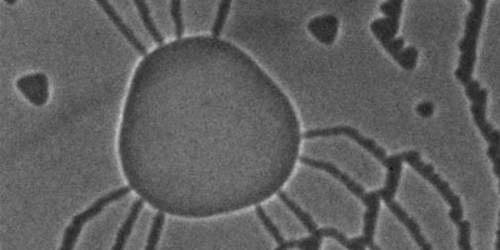
Membrane Holes Can Shrink, Grow, or Stay Put
Pores in a polymer film do not change size over time if they have just the right diameter, according to experiments. Read More »
Light Pushes and Pulls
Two forces coming from a light beam—one based on momentum transfer, the other on thermal effects—drive a tiny gold plate to move in opposite directions. Read More »
Atomic Impersonator
Calculations show that a carefully engineered laser pulse can induce an atom to emit light as if it were a different atom. Read More »
Making Rogue Waves with Wind and Water
Wind-generated waves in a ring-shaped water tank can spontaneously grow into single behemoth waves, mimicking a poorly understood ocean phenomenon. Read More »
Self-Spinning Grains Prove Granular Theory
Measurements of a two-dimensional “gas” made up of particles that spin when shaken bolsters a gas-like theory for granular materials. Read More »
Interferometer for Lighter Atoms
A new atom interferometer works at less extreme temperatures and with lighter atoms than previous designs, opening up a new route to precision measurements of fundamental constants. Read More »
Graphene Sliding on Graphene
Creating a bulge in a graphene sheet offers the first measurement of the shear forces between graphene layers, an essential factor in many graphene-based devices. Read More »
Bacteria Form Waveguides
A laser beam sent through a suspension of marine bacteria pulls the organisms into the beam, which focuses the light. Read More »
Vortices of Light on the Cheap
A simple laser setup has spontaneously produced nonuniform polarization patterns called vector vortices. Read More »
Probing Cell Squishiness
A new atomic force microscopy technique can map the elastic properties of living cells. Read More »
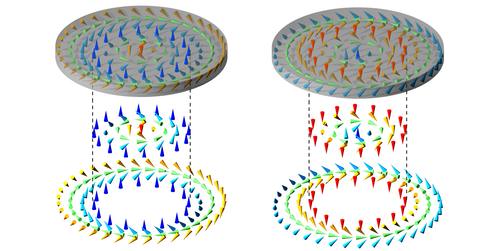
Field-Free Spin Patterns
A vortex-like magnetic spin structure inside a small disk of material is stable without an external magnetic field and might be useful for information storage or processing. Read More »
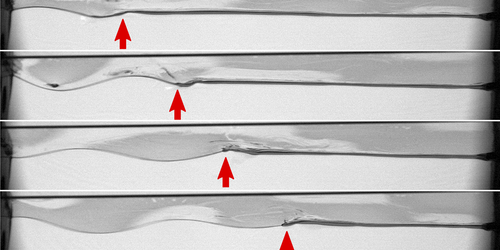
Liquid String Vibrations
A liquid microchannel—the line where three soap films meet—vibrates like a string whose diameter shrinks as the shaking force increases. Read More »
Taking Temperature in 2D
Electron microscopy can produce nanometer-scale maps of the thermal expansion of 2D materials, which may be important for the development of nanoelectronic devices. Read More »
Rinsing is Key to Removing Stains
Experiments show that rinsing clothes after washing can create imbalances in detergent concentration that pulls dirt out of the fabric. Read More »
Neutrinos with a Single Energy
Neutrinos in a beam have a wide range of energies, but a new trick allowed researchers to isolate fixed-energy neutrinos, which can improve the precision in future experiments. Read More »
Why Soft Solids Get Softer
Soft materials like gels and creams exhibit fatigue resulting from the stretching of their constituent fibers, according to experiments and simulations. Read More »
Stitching Together a Knit Theory
A new model predicts how each stitch in a knitted fabric will respond to a stretching force. Read More »
Nobel Prize—Lasers as Tools
The 2018 Nobel Prize in Physics goes to innovators in laser physics responsible for optical tweezers and high-intensity, ultrashort optical pulses. Read More »
How to Measure Viscosity Inside Cells
A noninvasive method measures the viscosity in a cell nucleus by observing the movement and fusion of cellular components. Read More »
Computing with Wi-Fi Waves
Experiments demonstrate that a room in a house or office building could act as an analog computer processing the microwaves used for Wi-Fi. Read More »
A Cooler Computer
A future computer might reduce heat production by timing operations to match naturally occurring temperature swings within the device. Read More »
Video—A Groovy Way to Harvest Dew
Dew condensing on an inclined, grooved surface rapidly forms large drops that roll quickly to the bottom for collection. Read More »
Two Types of Cooling Require Different Designs
Keeping food cold is thermodynamically different from cooling a hot circuit element—a distinction that is accounted for in the design of a new thermoelectric cooler. Read More »
Collection of Disks Mimics Earthquakes
A 2D array of disks under stress has replicated several statistical features of earthquakes, suggesting that this system is an accurate model of seismic phenomena. Read More »
X-Ray Movie Reveals Origin of Metal Splashing
X-ray imaging of a manufacturing technique has captured the formation of molten metal projectiles that produce imperfections. Read More »
Molecular Probe Uses a Polarization Flip
A new way of probing molecules with handedness involves a light pulse in which the polarization changes in the middle of a single wave cycle. Read More »
Cooling on the Negative Side
A new cooling technique targets negative ions, which are typically resistant to cooling methods that work with atoms and positive ions. Read More »
New Spaceship Sail Self-Centers
A technology for propelling spacecraft using a “sail” pushed by light has passed an initial test, with the prototype device staying centered in a laser beam. Read More »
Emitting Photons Is One Way to Be Cool
A device described in a new proposal would cool an object by causing it to radiate extra heat. Read More »
Sound-Driven Spin Waves
Sound waves generate large-amplitude spin waves that travel long distances in a magnetic film and that could be used to carry information. Read More »
Worm Viscosity
The activity of sludge worms can alter the viscosity of a fluid, a finding that could help researchers understand active systems in cellular biology. Read More »
Quantum Erasing with Phonons
Demonstrating quantum weirdness with vibration quanta called phonons shows that the particles can complement photons in quantum information technology. Read More »
Coin Flip Decides Material’s Fate
Stretching fibers until they fail reveals a correspondence between material strength and a 300-year-old math puzzle involving coin flips. Read More »
Possible Flare from Black Hole Merger
Astronomers have detected a brightening of a distant quasar that coincided with a potential gravitational-wave signature of a pair of merging black holes. Read More »
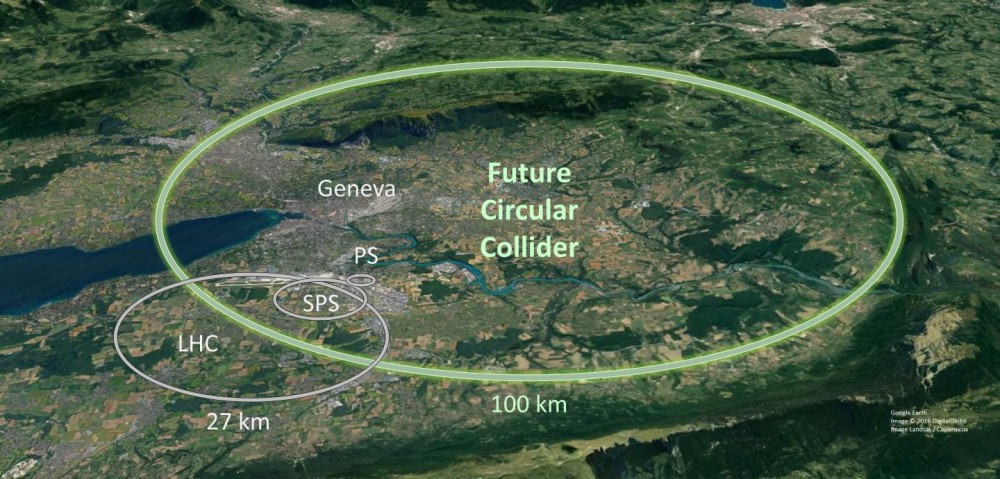
Europeans Decide on Particle Strategy
The CERN Council approved a strategy update that prioritizes a 100-km circular collider, while still developing other options for future particle physics projects. Read More »
A Jumpstart for Biochemistry
RNA can replicate in conditions that could be found on the early Earth, suggesting a possible step in the origin of life. Read More »
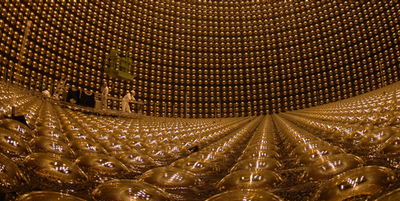
Powdering Up for Neutrinos
The search for neutrinos from past supernovae is getting an upgrade as Japan’s Super-Kamiokande experiment begins adding gadolinium powder to its giant water-based detector. Read More »
Limits on Purifying Quantum States
A new theoretical study identifies fundamental tradeoffs that limit the amount of noise reduction in quantum information systems. Read More »
Drawing a Line in the Sky: Astronomers Confront Satellite Threat
The astronomy community has released recommendations for mitigating the impact of thousands of internet-providing satellites that companies plan to launch in the coming years. Read More »
Single-Molecule Cloak
A nanoparticle can be made partially transparent by placing a molecule in front of it, forming a system that might work as an optical switch. Read More »
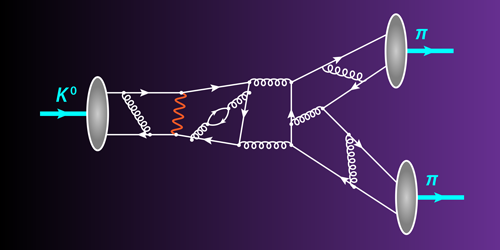
Kaon Decays Reevaluated
A rigorous calculation of a matter-antimatter asymmetry in kaon decays has twice the precision of a previous calculation, removing tension that had existed between theory and experiment. Read More »
Reproducing Space Plasma in the Lab
Electromagnetic fields rotate a plasma and produce conditions that resemble the region around a newly forming star. Read More »
Nobel Prize: Facing the Reality of Black Holes
Three scientists were recognized for proving that gravitational collapse can lead to a black hole and for observing the supermassive black hole at the center of our Galaxy. Read More »
Looking for Dark Matter in Neutron Star Light
Radio observations of neutron stars demonstrate a way to search for axions through their expected conversion to electromagnetic waves in a star’s magnetic field. Read More »
Vetting Neutral Nitrogen Vacancies
New experiments characterize the excitation levels of electrically neutral nitrogen-vacancy centers, information needed for quantum information applications. Read More »
Magnetic Oscillations at a Metal Surface
Predicted 40 years ago, magnetic Friedel oscillations are finally observed in the layers beneath an iron surface. Read More »
Hair Styling with Physics
Experiments show that hair-like bundles form different shapes depending on the speed at which they are dried. Read More »
Quantum Drones Take Flight
A small prototype of a drone-based quantum network has successfully relayed a quantum signal over a kilometer of free space. Read More »
Cosmic Ringtones in Pulsar Data?
A pulsar survey has detected a potential signal from low-frequency gravitational waves, which theorists are eager to explain. Read More »
Force Scanning on a Shaky Membrane
A microscope technique that visualizes small objects on a vibrating membrane could deliver atomically resolved MRI scans. Read More »
Doubly Strange Nucleus Observed
Particle physicists have detected a short-lived nucleus containing two strange quarks, whose properties could provide new insights into the behavior of other nuclear particles. Read More »
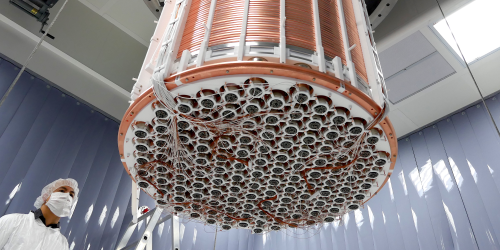
A 4D Fusion Puzzle
Duco Jansen explains how he, along with engineers at the ITER fusion experiment, will position 1000-ton parts shipped in from the four corners of the globe. Read More »
Wormholes Open for Transport
New theories of wormholes—postulated tunnels through spacetime—explore whether they could be traversable by humans. Read More »
Students Evaluate Online Teaching
A survey of physics students pinpoints strategies for improving the online teaching experience. Read More »
Robot Foragers
Using a swarm of puck-shaped robots, researchers simulate interactions between biological organisms and their environment. Read More »
Rising Tides on Black Holes
New calculations show that spinning black holes—unlike nonspinning ones—can be tidally deformed by a nonsymmetric gravitational field. Read More »
Measuring the Magnet that Measures the Muon
To precisely measure the magnetic moment of the muon, physicists first needed to precisely measure the field produced by the 680-ton magnet that guides the muons. Read More »
A Rockin’ Time for Space Missions
2021 may be the year of the space rock, with scientists combing through new (and old) samples from the Moon and asteroids, while plans for a pick-and-collect mission to Mars get under way. Read More »
Coffee, Donuts, and Semiconductors
During the Semiconductors for Breakfast meeting, researchers woke up to talks on light-emitting nanorods and hairy cavities. Read More »
Multi-Echo Imaging
With a one-pixel detector and a pulsed emitting device, researchers are able to produce a 3D image of a room from multiple echoes. Read More »
Keeping Time on Entropy’s Dime
An experiment with a nanoscale clock verifies that a clock’s entropy per tick increases as the clock is made more precise. Read More »
A Mott Meter
A new experimental method based on adsorption can indicate whether a material is a Mott insulator or a common insulator. Read More »
Uncertainty over First Stars
New analysis of nuclear reaction data finds holes in a theory about the first stars. Read More »
Spiral Arms in an Infant Galaxy
Astronomers have identified spiral arm features in a galaxy from the early Universe, suggesting that these arms can develop more rapidly than some theories predict. Read More »
Customizing Thermal Emission
Theorists have shown that patterned surfaces can transform the emission from a hot object into a polarized, focused light beam. Read More »
Improving the Human Machine
Robotics engineers turn their sights on making humans move more efficiently with the help of passive devices called exoskeletons. Read More »
Neutrinos Rising from the Floor
A neutrino background that could confound dark matter searches is now becoming an opportunity for probing new physics. Read More »
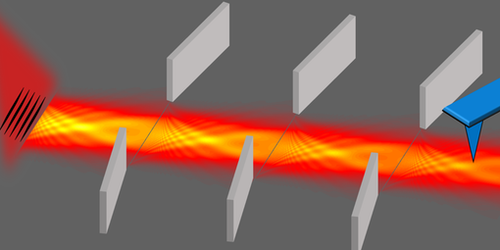
Guiding Waves by Snipping Their Edges
A new waveguide design uses a series of apertures, or slits, to keep waves confined to a narrow path. Read More »
Testing a 150-year-old Hydrodynamics Prediction
A new experiment finds that a sphere with “fins” maintains its orientation in a flowing fluid, despite a 19th century prediction that it would spin. Read More »
Valley-Polarized Jets in Graphene
Studying the current that flows in bilayer graphene, researchers have isolated electron jets associated with specific valley states. Read More »
Zapping Germs with LEDs
Michael Kneissl develops ultraviolet-light-emitting diodes that can neutralize bacteria and viruses in drinking water and on surfaces. Read More »
How Glaciers Set a Table
Laboratory experiments reveal the melting process that generates a commonly seen ice feature called a glacier table. Read More »
Fine Structure Constant Goes Big in Spin Ices
Inside a quantum spin ice, the constant that defines electromagnetic interactions is 10 times larger than normal, according to calculations. Read More »
Pedestrian Physics Walks Away with Two Ig Nobels
This year’s Ig Nobel prize winners include two groups of physicists studying how humans avoid—and sometimes don’t avoid—collisions while walking. Read More »
Nobel Prize: Complexity, from Atoms to Atmospheres
The 2021 Nobel Prize in Physics honors research on complex systems that undergo significant fluctuations, including glasses and Earth’s climate. Read More »
Reversing Flow in Charged Membranes
The process of osmosis is predicted—under certain conditions—to act in the opposite direction within charged membranes. Read More »
Dark Matter Alternative Passes Big Test
A cosmological model that doesn’t require dark matter has overcome a major hurdle in matching observations from the cosmic microwave background. Read More »
Topology Inside a Liquid Crystal
The orientation boundaries in a liquid crystal can be characterized by a topological charge that always sums to one, no matter the shape of the container. Read More »
Reversible Fabric Heats and Cools
A new theory proposes a reversible fabric that could potentially keep a person warm when worn one way and cool when flipped inside out. Read More »
Sun-Struck Scientist
Nicola Fox, who leads NASA’s heliophysics division, explains what it means to “touch the Sun.” Read More »
How to Survive Flying Too Close to the Sun
The Parker Solar Probe has flown through the Sun’s atmosphere—an unforgiving environment that poses a number of engineering challenges. Read More »
Pulsars Probe Early Universe
Astronomical observations of pulsars have provided new information about a possible phase transition in the early Universe. Read More »
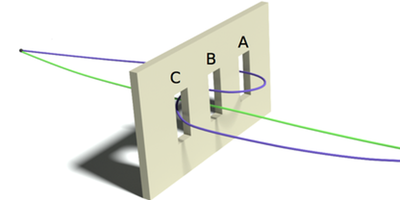
How to Find the Electron Starting Block
A new technique pinpoints, with picometer resolution, the location from which an emitted electron originates within a molecule. Read More »
Dark Energy Survey Hits a Triple
A large galaxy survey releases its three-year observations, providing key cosmological-parameter measurements that have double the precision of those previously released. Read More »
Antiproton Mirrors Proton
An antiproton experiment has shown to record precision that matter and antimatter particles have equal mass—confirming a basic tenet of the standard model of particle physics. Read More »
Mineral Candidates for Planet Interiors
Computer simulations uncover new high-pressure minerals that may explain the origin of Earth’s water and of Uranus’ and Neptune’s magnetic fields. Read More »
Diagramming Quantum Weirdness
Physicists try to develop a realist interpretation of quantum mechanics by drawing diagrams that represent causal connections and observer-acquired information. Read More »
Chasing an Unpredictable Quarry
Researchers explore the effects of random motion in a pursuit problem in which hounds chase a hare. Read More »
How Cotton Fibers Become Yarn
Experiments unravel the mysterious twisting process by which short fibers bind together into yarn. Read More »
Steering Toward a Quantum Advantage
New experiments make clear how quantum effects—in the form of quantum correlations—can make an engine perform better than classical limits. Read More »
Optical Sensor for a Pancreas-on-a-Chip
An optical sensor consisting of gold nanorods can provide real-time data on insulin production in an on-chip device mimicking the pancreas. Read More »
Magnetizing Diamonds with Light
By tuning the magnetic properties of a tiny levitating diamond, researchers control its orientation in a magnetic field. Read More »
Immune System’s Memory in an Evolving World
Researchers have identified strategies that our immune system uses to deal with highly evolving pathogens such as the flu virus and SARS-CoV-2. Read More »
High-Temperature Majoranas
A new proposal for generating Majorana zero modes—electronic states with potential for quantum computing—would not require subkelvin temperatures. Read More »
Scientific Dimensions of the Ukraine Crisis
At the APS April Meeting, physicists discussed ways to support Ukrainian scientists while keeping contact with Russian scientists. Read More »
Seismic Sensing Using Quantum Cryptography Network
An experiment demonstrates that quantum key distribution networks, which are part of highly secure cryptography schemes, can also detect and locate earthquakes. Read More »
Merged Black Hole on the Run
Analysis of the gravitational waves from a black hole merger suggests that the final black hole received a kick that will send it out of its galaxy. Read More »
Physics Scratches a Philosopher’s Itch
Philosopher Elise Crull muses over interpretations of quantum physics, focusing on experiments that cast doubt on our classical notions of causality. Read More »
Nanostructures Control Ultraviolet Light Generation
By etching nanostructures into ultraviolet-generating materials, researchers show that they can manipulate the outgoing light in ways that aren’t otherwise possible. Read More »
Hearing the Quantum Difference
At very low volume, a quantum optical microphone performs better than a classical device, and humans can hear the difference. Read More »
A Particle is Born: Making the Higgs Famous
Science communicators had a field day with the 2012 Higgs discovery, as it offered a chance to energize the public about fundamental physics research. Read More »
Birds of a Feather Hunt Differently
Tracking of bird movements shows that the animals don’t spread outward like molecules in a gas, as ecologists often assume. Read More »
Distant Memories Entangled
On the road to a quantum internet, researchers demonstrate entanglement of two memory elements located 12.5 km apart in an urban environment. Read More »
Bending under Big G
Most measurements of Newton’s gravity constant use stationary masses, but a new experiment measures the constant with wiggling metal beams. Read More »
Addressing WWW Production in Particle Collisions
The ATLAS Collaboration has detected triple W-boson production—a rare event that could eventually offer signs of new physics. Read More »
Shielding Qubits with Chemistry
The spin state of molecular qubits can be made more stable by changing the chemical environment in which the qubits sit. Read More »
Measuring the Similarity of Photons
A new optical device measures photon indistinguishability—an important property for future light-based quantum computers. Read More »
For the Love of Neutrinos
The CUPID-0 experiment has demonstrated a new detector technology that targets neutrinoless double beta decay. Read More »
Plant-Based Strategy for Harvesting Light
A new photodetector design borrows its light-gathering architecture from plants, offering a potential path to more efficient solar cells. Read More »
Nobel Prize: Quantum Entanglement Unveiled
The 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics honors research on the foundations of quantum mechanics, which opened up the quantum information frontier. Read More »
A Quantum Entanglement Assembly Line
A new experiment generates entanglement between many photons with a much higher probability than available methods, which could be a boon for quantum information applications. Read More »
A “Retro” Collider Design for a Higgs Factory
The Cool Copper Collider is a new proposal for a Higgs-producing linear collider that would be more compact than other collider designs. Read More »
Spacecraft Crash Changes Asteroid Orbit by 32 Minutes
NASA has confirmed that its DART spacecraft has altered the trajectory of the asteroid that it crashed into two weeks ago, demonstrating the potential of this tool for planetary defense. Read More »
Dwarf Galaxies Size Up Dark Matter Models
A proposed study of dwarf galaxies could give insight into whether dark matter particles interact with each other. Read More »
Dark Matter as an Intergalactic Heat Source
Spectra from quasars suggest that intergalactic gas may have been heated by a form of dark matter called dark photons. Read More »
A New Day Awaits Solar Neutrinos
Solar neutrinos are no longer the “stars” of neutrino research, but next-generation experiments characterizing these neutrinos may deepen our understanding of solar and neutrino physics. Read More »
Gaining Ground in Nuclear Fusion
Fusion researchers received an early holiday present with the confirmed measurement of a laser-induced fusion reaction that produced more energy than it consumed. Read More »
Why Wetting a Surface Can Increase Friction
Experiments suggest that hydrogen bonding explains why a wet surface can have nearly twice as much friction as a dry surface. Read More »
Targeting a Nuclear Halo
New modeling explains the relatively high fusion reaction probabilities of halo nuclei, which are composed of a dense core surrounded by a “satellite” of one or two nucleons. Read More »
Explaining Anomalies in Reactor Antineutrinos
A new analysis finds that discrepancies between reactor neutrino experiments and theory may be the result of errors in the analysis of electron data that form the basis of the neutrino predictions. Read More »
Sound Waves Mimic Gravity
A recently discovered acoustic effect allows a hot gas to simulate the gravity-induced convection within a star or giant planet. Read More »
A Laser-Based “Lightning Rod”
Experiments on a Swiss mountain demonstrate that a high-powered laser can influence the trajectory of lightning strikes—a step toward laser-based lightning protection. Read More »
Don’t Be Sold on Black Hole Imitators
The results of new simulations negate the argument that some objects thought to be black holes are instead hypothetical exotic systems called bosonic stars. Read More »
Secret of Flow-Induced Electric Currents Revealed
Vibrations are the main drivers of a mysterious process in which a liquid flow generates an electric current in the solid below it. Read More »
Turbulent Dance of Cloud Droplets
Rama Govindarajan models how turbulence influences the growth of droplets in clouds, information relevant to understanding the influence of these billowy masses on climate. Read More »
Beaming in a Spin Texture
Researchers use an optical vortex beam to create a stable pattern of electron spins in a thin layer of semiconductor material. Read More »
Publishing Science in a War Zone
The Ukrainian Journal of Physics has managed to keep publishing during the past year, offering an outlet for physicists in the war-torn country. Read More »
Quantum on a Microgram Scale
An experiment with an acoustic resonator demonstrates the quantum superposition of 1016 atoms—nearly matching the ability of matter interferometers to test quantumness on macroscopic scales. Read More »
Spinning Heat in Reverse
When spun fast enough, a cold object can transfer heat to a nearby hot object. Read More »
Stretching without Buckling
Materials that stretch on demand often bend in undesired directions, but a new theoretical model can produce stress-free designs that change shape without buckling. Read More »
Tweezers in Three Dimensions
A new kind of 3D optical lattice traps atoms using focused laser spots replicated in multiple planes and could eventually serve as a quantum computing platform. Read More »
Measuring Cosmic Expansion with a Lensed Supernova
Astronomers have demonstrated a new method for determining the Hubble constant that involves measuring the time delay between multiple images of a lensed supernova. Read More »
Bond Density Not Strength Controls Polymer Stickiness
Experiments show that the sticky behavior of so-called associative polymers is controlled by the density of bonding structures, contradicting theoretical predictions. Read More »
Active Matter Turns Pinwheels
The chaotic motion in a fluid of microscopic, actively moving rods can be harnessed to drive the rotation of a small propeller-like object. Read More »
Phonons on the Splitting Block
Using a “bad” acoustic mirror, physicists demonstrate a phonon beam splitter, a device that could one day be used to make phonon-based quantum logic gates. Read More »
Clock Comparison Limits Dark Matter
A search for oscillations in the frequencies of optical clocks has come up empty, implying new bounds on ultralight dark matter particles. Read More »
Probe of the Cosmos Using Lensed Gravitational Waves
The path of a gravitational wave passing near a galaxy can be bent, producing multiple signals that could help next-generation detectors measure the expansion of the Universe. Read More »
Getting a Heads-Up on Landslides from Space
A new method based on satellite data and network models can identify hillsides that may be at risk of catastrophic landslides. Read More »
Opening a Liquid Route to Fusion
A laser experiment provides a proof-of-principle test for an alternative fusion concept that uses targets made with liquid fuel rather than conventional frozen fuel. Read More »
Dark Star Hypothesis Sees the Light of Day
Recent data from the JWST space observatory has identified several objects that are consistent with dark matter powered stars. Read More »
AI Learns to Play with a Slinky
A new artificial intelligence algorithm can model the behavior of a set of objects, such as helical springs or pendulums, using a method that can extrapolate to objects that the algorithm hasn’t previously analyzed. Read More »
Measuring Thermal Migration
The slow drift of microscale features on a surface reveals the force driving atoms from the hot to the cold side of the material. Read More »
Breakthrough Prize for Quantum Field Theorists
The 2024 Breakthrough Prize in Fundamental Physics goes to John Cardy and Alexander Zamolodchikov for their work in applying field theory to diverse problems. Read More »
Quantum Ratchet Made Using an Optical Lattice
Researchers have turned an optical lattice into a ratchet that moves atoms from one site to the next. Read More »
Making a Beamline for Deep UV Spectroscopy
By using a pair of offset beams, researchers are able to generate femtosecond UV pulses that can be aimed directly into a target as a spectroscopic probe. Read More »
Golden Ticket to Stockholm
The envelopes for this year’s Nobel Prize winners are already sealed, but a survey of physicists offers ideas on future discoveries that are shoo-ins for Nobel recognition. Read More »
Nobel Prize: Flashes of Light Catch Electrons in the Act
The 2023 Nobel Prize in Physics honors the field of attosecond physics, which offers a nonblurry view of the fast-moving electrons inside atoms and molecules. Read More »
Unexpected Noise in Next-Generation Mirror Material
A crystalline reflective coating being considered for future gravitational-wave detectors exhibits peculiar noise features at cryogenic temperatures. Read More »
Five Protons Spew Out of Extreme Nucleus
A highly unstable nucleus that decays by emitting five protons has been observed, offering an extreme case for testing nuclear models. Read More »
Tension for a Hubble-Tension Solution
An early-Universe spike in dark energy could resolve a disagreement between two cosmic-expansion-rate measurements, but such a spike may conflict with observations of quasar spectra. Read More »
Electrons Lead Their Lattice by the Nose
Experiments with an unconventional superconductor show that a change in the properties of the material’s electrons can, unexpectedly, cause the material to become dramatically less stiff. Read More »
Control Knob Found for Viscous Fingers
The onset time for “viscous fingering”—an instability that can occur at a gas–liquid boundary—depends on the compressibility of the gas, offering a way to control the behavior. Read More »
Why It’s Hard to Break Plastics
The crack resistance of polymer materials is explained by a new model that incorporates a network of stretchable polymer chains. Read More »
Repeated Particle Measurements Disagree with Theory—What Now?
The experimental value of the muon’s magnetic moment disagrees with theoretical predictions, but some of those predictions also disagree with each other—a problem theorists are working to resolve. Read More »
Particles Flutter as They Fall
Experiments with small falling particles show that their orientations oscillate—which may help explain the settling of volcanic ash and the formation of snow. Read More »
A Moving Target for Quantum Advantage
Researchers have used quantum computers to solve difficult physics problems. But claims of a quantum “advantage” must wait as ever-improving algorithms boost the performance of classical computers. Read More »
Inertial-Confinement Fusion without Lasers
The recent breakthroughs in laser-based fusion have given a boost to a number of start-up companies—one of which has plans to replace the lasers with a high-speed projectile. Read More »
Material Hums a New Topological Tune
The sound waves in a fabricated material exhibit topological features in one, two, and three dimensions—demonstrating an acoustic version of a higher-order nodal-line semimetal. Read More »
A Sunny Path to Green Hydrogen
A theoretical study of metal oxides identifies potential candidate materials for generating hydrogen fuel from water and sunlight. Read More »
Voltage Control over Magnons
Researchers have demonstrated that magnetic spin waves called magnons can be controlled by voltage and thus could operate more efficiently as information carriers in future devices. Read More »
A New Source for Quantum Light
A new device consisting of a semiconductor ring produces pairs of entangled photons that could be used in a photonic quantum processor. Read More »
Making Sense of Handedness on a Lattice
David Kaplan has developed a lattice model for particles that are left- or right-handed, offering a firmer foundation for the theory of weak interactions. Read More »
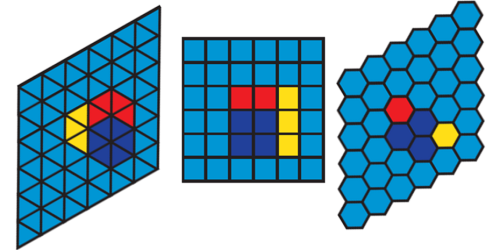
Shape Matters in Self-Assembly
A theoretical study of self-assembly finds that hexagon-shaped building blocks can form large structures faster than triangular or square blocks. Read More »
Quantum “Torch” Begins Its Relay
A quantum light source is touring European labs in preparation for the 2025 International Year of Quantum Science and Technology. Read More »
Sodium as a Green Substitute for Lithium in Batteries
Interest in developing batteries based on sodium has recently spiked because of concerns over the sustainability of lithium, which is found in most laptop and electric vehicle batteries. Read More »
Spinning Up Rydberg Atoms Extends Their Life
Researchers record the longest Rydberg-atom lifetime by placing strontium atoms in “circular” states, where the outer electrons move in planet-like orbits. Read More »
Avoiding Instabilities in Hydrogen-Spiked Flames
Experiments show the effects on combustion of adding hydrogen to natural gas—a fuel mixture that could reduce carbon emissions from power plants. Read More »
Cloud Computing under the Cover of Quantum
A secure method for cloud-based quantum computing harnesses the power of quantum physics to keep data confidential. Read More »
Atomic Spreading Produces Novel Superconductors
A liquid-like spreading of metal atoms on a topological material can generate a superconductor—one that might benefit quantum computing. Read More »
Mechanical Coupling to Spin Qubits
A vibrating nanobeam could be used to share information between distant solid-state spin qubits, potentially allowing use of these qubits in complex computations. Read More »
Measuring Qubits with “Time Travel” Protocol
Quantum sensing can benefit from entanglement protocols that can be interpreted as allowing qubits to go backward in time to choose an optimal initial state. Read More »
Temperature Affects Aging in Granular Materials
Experiments on a bed of plastic beads reveal a temperature-dependent stiffening over time, which appears to be related to molecular-scale deformations. Read More »
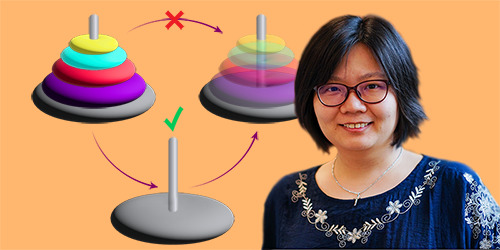
“Catalyzing” Quantum Information
Nelly Ng studies “quantum catalysts”—extra qubits or other elements that can help perform a quantum information process, in the same way that an extra tower helps solve a classic logic game. Read More »
New Quantum Effect in Textbook Chemistry Law
The observation of quantum modifications to a well-known chemical law could lead to performance improvements for quantum information storage. Read More »
Dark Matter Search in Gravitational-Wave Data
An analysis of gravitational data from the LIGO detector sets new limits on a wave-like form of dark matter called scalar-field dark matter. Read More »
Materials Found to Be Surprisingly Transparent to Orbital Currents
Orbital currents can efficiently flow through a variety of materials—a promising result for future orbitronics devices. Read More »
LHC Data Constrain Multiple Higgs Models
New experimental results from the Large Hadron Collider argue against the existence of multiple Higgs bosons, as predicted in certain “beyond-standard-model” theories. Read More »
Positronium Cooled to Record Low Temperature
A short-lived combination of an electron and an antielectron has been cooled with lasers to near absolute zero—a step toward tackling fundamental questions about matter and antimatter. Read More »
Measuring Particle Diffusion with the Countoscope
A new method for studying the behavior of multiparticle systems relies on a simple “head count” of particles in imaginary boxes. Read More »
Drip Physics Produces Flexible Stalactite-Like Surface
By repeatedly applying coats of a hardening polymer to a surface, researchers have created rubbery stalactite-like formations that could be useful in soft robotics. Read More »
Information Flow in Molecular Machines
A theoretical model shows that exchange of information plays a key role in the molecular machines found in biological cells. Read More »
Supersolids Shown to Host Vortices
The experimental confirmation of supersolid vortices opens the prospect of making and studying laboratory analogues of rotating neutron stars. Read More »
Cracking the Challenge of Quantum Error Correction
Researchers at Google Quantum AI have demonstrated “below-threshold” error correction, a necessary condition for building noise-resistant quantum computers that are sufficiently large to perform useful computations. Read More »
Making Waves in the Debate over Light-Induced Superconductivity
New experiments with cuprate materials explore a connection between so-called charge-density waves and a light-induced state that resembles superconductivity. Read More »
Mapping Spin Waves with a Strobe Light
A method for imaging spin waves in magnetic materials uses flash-like intensity variations in a laser beam to capture the wave motion at specific moments in time. Read More »
Improving Models of Landslide Speed
Measurements of grains flowing down an inclined plane have uncovered general principles that may help researchers model rockslides and other granular flows. Read More »
Monster Shocks Could Explain Radio Bursts
Powerful shock waves around magnetized neutron stars may be the source of mysterious radio bursts that are observed across the sky. Read More »
Curtain Rises on the Year of Quantum
The official launch of the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology happened in Paris, with a push to make “quantum” more accessible to all. Read More »
Cold Calculus: Modeling Heat Exchange in the Arctic
A new model captures the flow of heat from ocean water into floating ice, providing an important input for efforts to predict future melting in the Arctic. Read More »
An Ultrahigh Neutrino Detection Makes Waves
A new underwater neutrino experiment—for now, only partially installed—has detected what appears to be the highest-energy cosmic neutrino observed to date. Read More »
New Strategy in the Hunt for Quantum Gravity
Predictions of theories that combine quantum mechanics with gravity could be observed using highly sensitive photon detection in a tabletop experiment. Read More »
No Easy Fix for Cosmology’s “Other” Tension
The S8 tension—a disagreement between cosmic-clumpiness measurements—is not going away, according to a new analysis of galaxy lensing data. Read More »